Erbb4 Deletion From Inhibitory Interneurons Causes Psychosis-Relevant Neuroimaging Phenotypes
- PMID: 36573631
- PMCID: PMC10154722
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbac192
Erbb4 Deletion From Inhibitory Interneurons Causes Psychosis-Relevant Neuroimaging Phenotypes
Abstract
Background and hypothesis: Converging lines of evidence suggest that dysfunction of cortical GABAergic inhibitory interneurons is a core feature of psychosis. This dysfunction is thought to underlie neuroimaging abnormalities commonly found in patients with psychosis, particularly in the hippocampus. These include increases in resting cerebral blood flow (CBF) and glutamatergic metabolite levels, and decreases in ligand binding to GABAA α5 receptors and to the synaptic density marker synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (SV2A). However, direct links between inhibitory interneuron dysfunction and these neuroimaging readouts are yet to be established. Conditional deletion of a schizophrenia susceptibility gene, the tyrosine kinase receptor Erbb4, from cortical and hippocampal inhibitory interneurons leads to synaptic defects, and behavioral and cognitive phenotypes relevant to psychosis in mice.
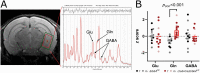
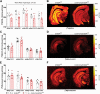
Study design: Here, we investigated how this inhibitory interneuron disruption affects hippocampal in vivo neuroimaging readouts. Adult Erbb4 conditional mutant mice (Lhx6-Cre;Erbb4F/F, n = 12) and their wild-type littermates (Erbb4F/F, n = 12) were scanned in a 9.4T magnetic resonance scanner to quantify CBF and glutamatergic metabolite levels (glutamine, glutamate, GABA). Subsequently, we assessed GABAA receptors and SV2A density using quantitative autoradiography.
Results: Erbb4 mutant mice showed significantly elevated ventral hippccampus CBF and glutamine levels, and decreased SV2A density across hippocampus sub-regions compared to wild-type littermates. No significant GABAA receptor density differences were identified.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that specific disruption of cortical inhibitory interneurons in mice recapitulate some of the key neuroimaging findings in patients with psychosis, and link inhibitory interneuron deficits to non-invasive measures of brain function and neurochemistry that can be used across species.
Keywords: Erbb4; hippocampus; inhibitory interneurons; mice; neuroimaging; psychosis.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center.
Conflict of interest statement
In the last 3 years, JMS has been principal investigator or sub-investigator on studies sponsored by Takeda, Janssen, and Lundbeck Plc. He has attended an Investigators’ meeting run by Allergan Plc. All other authors have declared that there are no conflicts of interest in relation to the subject of this study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prefrontal and Hippocampal Parvalbumin Interneurons in Animal Models for Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Schizophr Bull. 2024 Jan 1;50(1):210-223. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbad123. Schizophr Bull. 2024. PMID: 37584417 Free PMC article.
-
Neuregulin 1 Type I Overexpression Is Associated with Reduced NMDA Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Signaling in Hippocampal Interneurons Expressing PV or CCK.eNeuro. 2018 May 8;5(2):ENEURO.0418-17.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0418-17.2018. eCollection 2018 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 29740596 Free PMC article.
-
Nrg1 haploinsufficiency alters inhibitory cortical circuits.Neurobiol Dis. 2021 Sep;157:105442. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105442. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Neurobiol Dis. 2021. PMID: 34246770
-
ErbB4 signaling in dopaminergic axonal projections increases extracellular dopamine levels and regulates spatial/working memory behaviors.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Nov;23(11):2227-2237. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.132. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28727685 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic mechanisms of hippocampal hyperactivity in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2015 Sep;167(1-3):4-11. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.09.041. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Schizophr Res. 2015. PMID: 25449711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of diazepam on hippocampal blood flow in people at clinical high risk for psychosis.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Aug;49(9):1448-1458. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01864-9. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38658738 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Investigating brain alterations in the Dp1Tyb mouse model of Down syndrome.Neurobiol Dis. 2023 Nov;188:106336. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106336. Neurobiol Dis. 2023. PMID: 38317803 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of hippocampal activity in schizophrenia with levetiracetam: a randomized, double-blind, cross-over, placebo-controlled trial.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Mar;49(4):681-689. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01730-0. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 37833590 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Modelling the overlap and divergence of autistic and schizotypal traits on hippocampal subfield volumes and regional cerebral blood flow.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Jan;29(1):74-84. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02302-w. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 37891246 Free PMC article.
-
Prefrontal and Hippocampal Parvalbumin Interneurons in Animal Models for Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Schizophr Bull. 2024 Jan 1;50(1):210-223. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbad123. Schizophr Bull. 2024. PMID: 37584417 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

