Repurposing antimalarial artesunate for the prophylactic treatment of depression: Evidence from preclinical research
- PMID: 36573693
- PMCID: PMC9847619
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.2833
Repurposing antimalarial artesunate for the prophylactic treatment of depression: Evidence from preclinical research
Abstract
Introduction: Several studies have linked inflammation and oxidative stress with the pathogenesis of depression. Artesunate is a commonly used medication to treat malaria and has been shown to produce antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects. However, its prophylactic effects on depression and depression-related brain pathology are unknown.
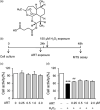
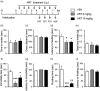
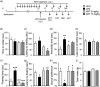
Methods: In Experiment 1, using a PC12 cell line, we investigated whether artesunate can prevent hydrogen peroxide (H2 O2 )-induced oxidative injury that mimics oxidative stress commonly observed in the depressed brain. Next, using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced mouse model of depression, we investigated whether artesunate can prevent behavioral deficits observed in the open field test, novelty-suppressed feeding test, sucrose preference test, forced swimming test, and tail suspension procedure.
Results: We found that artesunate significantly prevented a H2 O2 -induced reduction in PC12 cell activity, suggesting its antioxidant potential. We also found that mice pretreated with artesunate (5, 15 mg/kg) intraperitoneally (i.p.) prior to the LPS (.8 mg/kg, i.p.) treatment showed fewer and less severe depression- and anxiety-like behaviors than the LPS-treated control mice.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that artesunate produces antioxidant effect, as well as antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. Importantly, our findings first demonstrate that artesunate can prevent LPS-induced depression- and anxiety-like symptoms, strongly suggesting its prophylactic potential in the treatment of depression and, perhaps, other psychiatric disorders associated with inflammation and oxidative stress.
Keywords: artesunate; depression; inflammation; lipopolysaccharide; mouse.
© 2022 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Honokiol abrogates lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive like behavior by impeding neuroinflammation and oxido-nitrosative stress in mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Dec 5;744:124-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.09.049. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25446914
-
Intranasal lipopolysaccharide administration prevents chronic stress-induced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Dec 1;200:108816. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108816. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34599975
-
Xenon produces rapid antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects in lipopolysaccharide-induced depression mice model.Neuroreport. 2020 Mar 25;31(5):387-393. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001415. Neuroreport. 2020. PMID: 32106142
-
Lipopolysaccharide induced anxiety- and depressive-like behaviour in mice are prevented by chronic pre-treatment of esculetin.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Jan 12;611:106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.11.031. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 26620836
-
Enhancing the antimalarial activity of artesunate.Parasitol Res. 2020 Sep;119(9):2749-2764. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06786-1. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Parasitol Res. 2020. PMID: 32638101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artesunate Exerts Organ- and Tissue-Protective Effects by Regulating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Autophagy, Apoptosis, and Fibrosis: A Review of Evidence and Mechanisms.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 3;13(6):686. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060686. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alkaloidal Extracts from Avicennia africana P. Beauv. (Avicenniaceae) Leaf: An Antiplasmodial, Antioxidant, and Erythrocyte Viable.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024 Jan 9;2024:4541581. doi: 10.1155/2024/4541581. eCollection 2024. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38235482 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-Species Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Scaling for Drug Repurposing of Pyronaridine and Artesunate.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):6998. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136998. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000107 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of artesunate in retinal diseases: from mechanism to clinical applications.Int J Ophthalmol. 2025 Jun 18;18(6):1146-1151. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2025.06.22. eCollection 2025. Int J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40534801 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akhondzadeh, S. , Jafari, S. , Raisi, F. , Nasehi, A. A. , Ghoreishi, A. , Salehi, B. , Mohebbi‐Rasa, S. , Raznahan, M. , & Kamalipour, A. (2009). Clinical trial of adjunctive celecoxib treatment in patients with major depression: A double blind and placebo controlled trial. Depression and Anxiety, 26(7), 607–611. 10.1002/da.20589 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clark, R. L. , Arima, A. , Makori, N. , Nakata, Y. , Bernard, F. , Gristwood, W. , Harrell, A. , White, T. E. K. , & Wier, P. J. (2008). Artesunate: developmental toxicity and toxicokinetics in monkeys. Birth Defects Research. Part B, Developmental and Reproductive Toxicology, 83(4), 418–434. 10.1002/bdrb.20163 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

