Investigating changes in incidence and severity of pediatric appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada: an interrupted time series analysis
- PMID: 36574211
- PMCID: PMC9792923
- DOI: 10.1007/s12519-022-00656-9
Investigating changes in incidence and severity of pediatric appendicitis during the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada: an interrupted time series analysis
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
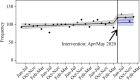
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence and severity of pediatric appendicitis during the COVID‑19 pandemic.World J Pediatr. 2023 Jul;19(7):710-712. doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00712-y. Epub 2023 Apr 11. World J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37039925 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to "Incidence and severity of pediatric appendicitis during the COVID‑19 pandemic".World J Pediatr. 2023 Jul;19(7):713. doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00713-x. Epub 2023 Apr 11. World J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37039926 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Long-Term Effect of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Management of Pediatric Appendicitis.Pediatr Ann. 2022 Jul;51(7):e266-e269. doi: 10.3928/19382359-20220504-03. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Pediatr Ann. 2022. PMID: 35858217
-
Incidence of Perforated Appendicitis during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons to Be Considered in the Second Wave.J Gastrointest Surg. 2021 Sep;25(9):2404-2406. doi: 10.1007/s11605-021-04915-4. Epub 2021 Feb 8. J Gastrointest Surg. 2021. PMID: 33555522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An Accountable Care Organization Maintains Access for Appendicitis During the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Surg Res. 2023 Nov;291:336-341. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2023.06.004. Epub 2023 Jun 22. J Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37506433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reasons for Delayed Diagnosis of Pediatric Acute Appendicitis during the COVID-19 Era: A Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Aug 2;13(15):2571. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152571. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incidence and severity of pediatric appendicitis during the COVID‑19 pandemic.World J Pediatr. 2023 Jul;19(7):710-712. doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00712-y. Epub 2023 Apr 11. World J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37039925 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Management and outcomes of acute appendicitis in children during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pediatr Surg Int. 2023 Nov 28;40(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s00383-023-05594-9. Pediatr Surg Int. 2023. PMID: 38017246 Free PMC article.
-
Response to "Incidence and severity of pediatric appendicitis during the COVID‑19 pandemic".World J Pediatr. 2023 Jul;19(7):713. doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00713-x. Epub 2023 Apr 11. World J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37039926 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Polcwiartek LB, Polcwiartek C, Andersen MP, Østergaard L, Broccia MD, Gislason GH, et al. Consequences of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) lockdown on infection-related hospitalizations among the pediatric population in Denmark. Eur J Pediatr. 2021;180:1955–1963. doi: 10.1007/s00431-021-03934-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angoulvant F, Ouldali N, Yang DD, Filser M, Gajdos V, Rybak A, et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: impact caused by school closure and national lockdown on pediatric visits and admissions for viral and nonviral infections—a time series analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;72:319–322. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa710. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

