Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen is a viral transcription activator that is essential for viral genome maintenance
- PMID: 36574443
- PMCID: PMC9829177
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011039
Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen is a viral transcription activator that is essential for viral genome maintenance
Abstract
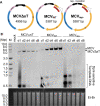
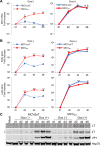
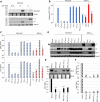
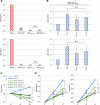
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV) is a small DNA tumor virus that persists in human skin and causes Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) in immunocompromised individuals. The multi-functional protein MCV small T (sT) activates viral DNA replication by stabilizing large T (LT) and promotes cell transformation through the LT stabilization domain (LTSD). Using MCVΔsT, a mutant MCV clone that ablates sT, we investigated the role of sT in MCV genome maintenance. sT was dispensable for initiation of viral DNA replication, but essential for maintenance of the MCV genome and activation of viral early and late gene expression for progression of the viral lifecycle. Furthermore, in phenotype rescue studies, exogenous sT activated viral DNA replication and mRNA expression in MCVΔsT through the LTSD. While exogenous LT expression, which mimics LT stabilization, increased viral DNA replication, it did not activate viral mRNA expression. After cataloging transcriptional regulator proteins by proximity-based MCV sT-host protein interaction analysis, we validated LTSD-dependent sT interaction with four transcriptional regulators: Cux1, c-Jun, BRD9, and CBP. Functional studies revealed Cux1 and c-Jun as negative regulators, and CBP and BRD9 as positive regulators of MCV transcription. CBP inhibitor A-485 suppressed sT-induced viral gene activation in replicating MCVΔsT and inhibited early gene expression in MCV-integrated MCC cells. These results suggest that sT promotes viral lifecycle progression by activating mRNA expression and capsid protein production through interaction with the transcriptional regulators. This activity is essential for MCV genome maintenance, suggesting a critical role of sT in MCV persistence and MCC carcinogenesis.
Copyright: © 2022 Rapchak et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small Tumor Antigen Activates Matrix Metallopeptidase-9 Gene Expression for Cell Migration and Invasion.J Virol. 2020 Sep 15;94(19):e00786-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00786-20. Print 2020 Sep 15. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32669331 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Large T Antigen Unique Domain Regulates Its Own Protein Stability and Cell Growth.Viruses. 2020 Sep 18;12(9):1043. doi: 10.3390/v12091043. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32962090 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive Merkel cell carcinoma cells do not require expression of the viral small T antigen.J Invest Dermatol. 2013 Aug;133(8):2059-64. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.82. Epub 2013 Feb 25. J Invest Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23439392
-
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus: Oncogenesis in a Stable Genome.Viruses. 2021 Dec 30;14(1):58. doi: 10.3390/v14010058. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 35062263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Merkel cell carcinoma: a virus-induced human cancer.Annu Rev Pathol. 2012;7:123-44. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130227. Epub 2011 Sep 13. Annu Rev Pathol. 2012. PMID: 21942528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of molecular mechanisms driving Merkel cell polyomavirus oncogene transcription and tumorigenic potential.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Aug 30;19(8):e1011598. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011598. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37647312 Free PMC article.
-
Polyomavirus ALTOs, but not MTs, downregulate viral early gene expression by activating the NF-κB pathway.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 25:2024.05.24.595774. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.24.595774. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2403133121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2403133121. PMID: 38826197 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Co-Infection in HIV/AIDS Individuals: Clinical Diagnosis, Consequences and Treatments.Pathogens. 2025 Feb 2;14(2):134. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14020134. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40005510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Virus Replication by BK Polyomavirus Small T Antigen.J Virol. 2023 Mar 30;97(3):e0007723. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00077-23. Epub 2023 Mar 14. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 36916919 Free PMC article.
-
Polyomavirus ALTOs, but not MTs, downregulate viral early gene expression by activating the NF-κB pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2403133121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2403133121. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39141346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schowalter RM, Pastrana DV, Pumphrey KA, Moyer AL, Buck CB. Merkel cell polyomavirus and two previously unknown polyomaviruses are chronically shed from human skin. Cell Host Microbe. 2010;7(6):509–15. Epub 2010/06/15. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.05.006 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2919322. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

