ERK and c-Myc signaling in host-derived tumor endothelial cells is essential for solid tumor growth
- PMID: 36574698
- PMCID: PMC9910475
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2211927120
ERK and c-Myc signaling in host-derived tumor endothelial cells is essential for solid tumor growth
Abstract
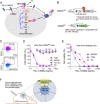
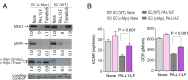
The limited efficacy of the current antitumor microenvironment strategies is due in part to the poor understanding of the roles and relative contributions of the various tumor stromal cells to tumor development. Here, we describe a versatile in vivo anthrax toxin protein delivery system allowing for the unambiguous genetic evaluation of individual tumor stromal elements in cancer. Our reengineered tumor-selective anthrax toxin exhibits potent antiproliferative activity by disrupting ERK signaling in sensitive cells. Since this activity requires the surface expression of the capillary morphogenesis protein-2 (CMG2) toxin receptor, genetic manipulation of CMG2 expression using our cell-type-specific CMG2 transgenic mice allows us to specifically define the role of individual tumor stromal cell types in tumor development. Here, we established mice with CMG2 only expressed in tumor endothelial cells (ECs) and determined the specific contribution of tumor stromal ECs to the toxin's antitumor activity. Our results demonstrate that disruption of ERK signaling only within tumor ECs is sufficient to halt tumor growth. We discovered that c-Myc is a downstream effector of ERK signaling and that the MEK-ERK-c-Myc central metabolic axis in tumor ECs is essential for tumor progression. As such, disruption of ERK-c-Myc signaling in host-derived tumor ECs by our tumor-selective anthrax toxins explains their high efficacy in solid tumor therapy.
Keywords: ERK signaling; anthrax lethal toxin; c-Myc; endothelial cells; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anthrax lethal toxin exerts potent metabolic inhibition of the cardiovascular system.mBio. 2024 Dec 11;15(12):e0216024. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02160-24. Epub 2024 Nov 7. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39508614 Free PMC article.
-
The receptors that mediate the direct lethality of anthrax toxin.Toxins (Basel). 2012 Dec 27;5(1):1-8. doi: 10.3390/toxins5010001. Toxins (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23271637 Free PMC article.
-
Solid tumor therapy by selectively targeting stromal endothelial cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 12;113(28):E4079-87. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600982113. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27357689 Free PMC article.
-
The dark sides of capillary morphogenesis gene 2.EMBO J. 2012 Jan 4;31(1):3-13. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.442. Epub 2011 Dec 6. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22215446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between anthrax toxin receptors and protective antigen.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005 Feb;8(1):106-12. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.12.005. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15694864 Review.
Cited by
-
ATP depletion in anthrax edema toxin pathogenesis.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Apr 1;21(4):e1013017. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013017. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40168442 Free PMC article.
-
A positive feedback loop between PFKP and c-Myc drives head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression.Mol Cancer. 2024 Jul 9;23(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02051-6. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38982480 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Butyrate to Inhibit Colonic Cancer Cell Growth Is Cell Type-Specific and Apoptosis-Dependent.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 14;16(4):529. doi: 10.3390/nu16040529. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398853 Free PMC article.
-
Vilazodone Alleviates Neurogenesis-Induced Anxiety in the Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Female Rat Model: Role of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;61(11):9060-9077. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04142-3. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38584231 Free PMC article.
-
STK32C promotes colon tumor progression through activating c-MYC signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Jun 14;82(1):235. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05773-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40515843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bejarano L., Jordao M. J. C., Joyce J. A., Therapeutic targeting of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 11, 933–959 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H., Integrating the anti-VEGF-A humanized monoclonal antibody bevacizumab with chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer. Clin. Colorectal. Cancer 4, S62–68 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H., et al. , Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 2335–2342 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Schmittnaegel M., et al. , Dual angiopoietin-2 and VEGFA inhibition elicits antitumor immunity that is enhanced by PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Sci. Transl. Med. 9, eaak9670 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

