Optic neuromyelitis after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36574993
- PMCID: PMC9806042
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2022-252309
Optic neuromyelitis after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
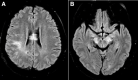
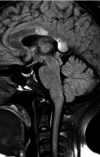
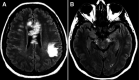
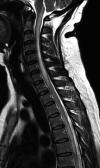
Neuromyelitis optica is an autoimmune demyelinating astrocytopathy of the central nervous system that primarily affects the optic nerve and spinal cord. It is considered a multifactorial disease associated with antibodies against aquaporin 4, with complement cascade activation and lymphocytic infiltration leading to axonal loss and causing significant morbidity and disability. In addition, cases of inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system have been described after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, mainly acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Also, a few cases of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, mostly aquaporin 4+, have been reported. We describe a patient who developed symptoms suggestive of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis the next day after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2. Three months later, a longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis compatible with aquaporin 4+ neuromyelitis optica was successfully treated with an interleukin 6 inhibitor. There is no proven association and research is needed to establish whether optic neuromyelitis is related to vaccination; this is a single case report from which no conclusion can be drawn.
Keywords: COVID-19; Immunological products and vaccines; Immunology; Neuroimaging; Neurology (drugs and medicines).
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Seropositive Neuromyelitis Optica in a Case of Undiagnosed Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Neuro-Rheumatological Conundrum.Qatar Med J. 2022 Jul 7;2022(3):29. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2022.29. eCollection 2022. Qatar Med J. 2022. PMID: 35864917 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Inflammatory Diseases of the Central Nervous System After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2022 Nov 21;10(1):e200063. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200063. Print 2023 Jan. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2022. PMID: 36411077 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal cord involvement in COVID-19: A review.J Spinal Cord Med. 2023 May;46(3):390-404. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2021.1888022. Epub 2021 Mar 11. J Spinal Cord Med. 2023. PMID: 33705268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder following seasonal influenza vaccination.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019 May;30:110-113. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2019.01.052. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 30769255
-
Aquaporin-4 IgG neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder onset after Covid-19 vaccination: Systematic review.J Neuroimmunol. 2022 Dec 15;373:577994. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2022.577994. Epub 2022 Oct 28. J Neuroimmunol. 2022. PMID: 36332464
Cited by
-
Complement and COVID-19: Three years on, what we know, what we don't know, and what we ought to know.Immunobiology. 2023 May;228(3):152393. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2023.152393. Epub 2023 May 11. Immunobiology. 2023. PMID: 37187043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurological Adverse Reactions to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2023 May 30;21(2):222-239. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2023.21.2.222. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37119215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
