Hydrogen Sulfide Modulates Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Heart Failure
- PMID: 36575984
- PMCID: PMC9852013
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321326
Hydrogen Sulfide Modulates Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Heart Failure
Abstract
Background: Hydrogen sulfide is a critical endogenous signaling molecule that exerts protective effects in the setting of heart failure. Cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE), 1 of 3 hydrogen-sulfide-producing enzyme, is predominantly localized in the vascular endothelium. The interaction between the endothelial CSE-hydrogen sulfide axis and endothelial-mesenchymal transition, an important pathological process contributing to the formation of fibrosis, has yet to be investigated.
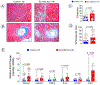
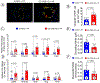
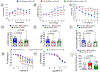
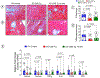
Methods: Endothelial-cell-specific CSE knockout and Endothelial cell-CSE overexpressing mice were subjected to transverse aortic constriction to induce heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Cardiac function, vascular reactivity, and treadmill exercise capacity were measured to determine the severity of heart failure. Histological and gene expression analyses were performed to investigate changes in cardiac fibrosis and the activation of endothelial-mesenchymal transition.
Results: Endothelial-cell-specific CSE knockout mice exhibited increased endothelial-mesenchymal transition and reduced nitric oxide bioavailability in the myocardium, which was associated with increased cardiac fibrosis, impaired cardiac and vascular function, and worsened exercise performance. In contrast, genetic overexpression of CSE in endothelial cells led to increased myocardial nitric oxide, decreased endothelial-mesenchymal transition and cardiac fibrosis, preserved cardiac and endothelial function, and improved exercise capacity.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that endothelial CSE modulates endothelial-mesenchymal transition and ameliorate the severity of pressure-overload-induced heart failure, in part, through nitric oxide-related mechanisms. These data further suggest that endothelium-derived hydrogen sulfide is a potential therapeutic for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
Keywords: endothelial cell; fibrosis; heart failure; hydrogen sulfide.
Figures



References
-
- Bozkurt B, Hershberger RE, Butler J, Grady KL, Heidenreich PA, Isler ML, Kirklin JK and Weintraub WS. 2021 ACC/AHA Key Data Elements and Definitions for Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Data Standards (Writing Committee to Develop Clinical Data Standards for Heart Failure). Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2021:HCQ0000000000000102. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Cheng S, Delling FN, Elkind MSV, Evenson KR, Ferguson JF, Gupta DK, Khan SS, Kissela BM, Knutson KL, Lee CD, Lewis TT, Liu J, Loop MS, Lutsey PL, Ma J, Mackey J, Martin SS, Matchar DB, Mussolino ME, Navaneethan SD, Perak AM, Roth GA, Samad Z, Satou GM, Schroeder EB, Shah SH, Shay CM, Stokes A, VanWagner LB, Wang NY, Tsao CW, American Heart Association Council on E, Prevention Statistics C and Stroke Statistics S. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2021 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143:e254–e743. - PubMed
-
- Nabel EG and Braunwald E. A tale of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:54–63. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich PA, Albert NM, Allen LA, Bluemke DA, Butler J, Fonarow GC, Ikonomidis JS, Khavjou O, Konstam MA, Maddox TM, Nichol G, Pham M, Pina IL, Trogdon JG, American Heart Association Advocacy Coordinating C, Council on Arteriosclerosis T, Vascular B, Council on Cardiovascular R, Intervention, Council on Clinical C, Council on E, Prevention and Stroke C. Forecasting the impact of heart failure in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Heart Fail. 2013;6:606–19. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

