Evaluation of immunogenicity post two doses of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, Covaxin after six months
- PMID: 36576223
- PMCID: PMC9891675
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2156753
Evaluation of immunogenicity post two doses of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, Covaxin after six months
Abstract
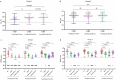
We have evaluated the immunogenicity of two dose of Covaxin given at a one-month interval to two adult populations, i.e. COVID-19 naïve-vaccinated individuals (n = 118) and COVID-19 recovered individuals (n = 128) with the vaccination. The immune response in the study population were assessed at three follow-ups, namely at one month post first dose, one and six months after the second dose. The persistence of S1RBD IgG and neutralizing antibodies for six months post vaccination was observed at different time intervals. The enhanced immune response was observed in both the participant groups. The study emphasizes the need for a booster dose post six months of vaccination.
Keywords: Covaxin; Sars-CoV-2; adult population; immunogenicity.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Ella R, Vadrevu KM, Jogdand H, Prasad S, Reddy S, Sarangi V, Ganneru B, Sapkal G, Yadav P, Abraham P, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, BBV152: a double-blind, randomised, phase 1 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21(5):637–46. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30942-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Annexes to the interim recommendations for use of the bharat biotech BBV152 COVAXIN® vaccine against COVID-19. [accessed 2022 Sep15]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-vaccines-SAGE-reco....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
