Deep learning assisted contrast-enhanced CT-based diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis of oral cancer: a retrospective study of 1466 cases
- PMID: 36576543
- PMCID: PMC9795159
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-022-09355-5
Deep learning assisted contrast-enhanced CT-based diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis of oral cancer: a retrospective study of 1466 cases
Abstract
Objectives: Lymph node (LN) metastasis is a common cause of recurrence in oral cancer; however, the accuracy of distinguishing positive and negative LNs is not ideal. Here, we aimed to develop a deep learning model that can identify, locate, and distinguish LNs in contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) images with a higher accuracy.
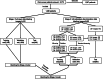
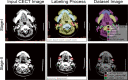
Methods: The preoperative CECT images and corresponding postoperative pathological diagnoses of 1466 patients with oral cancer from our hospital were retrospectively collected. In stage I, full-layer images (five common anatomical structures) were labeled; in stage II, negative and positive LNs were separately labeled. The stage I model was innovatively employed for stage II training to improve accuracy with the idea of transfer learning (TL). The Mask R-CNN instance segmentation framework was selected for model construction and training. The accuracy of the model was compared with that of human observers.
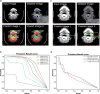
Results: A total of 5412 images and 5601 images were labeled in stage I and II, respectively. The stage I model achieved an excellent segmentation effect in the test set (AP50-0.7249). The positive LN accuracy of the stage II TL model was similar to that of the radiologist and much higher than that of the surgeons and students (0.7042 vs. 0.7647 (p = 0.243), 0.4216 (p < 0.001), and 0.3629 (p < 0.001)). The clinical accuracy of the model was highest (0.8509 vs. 0.8000, 0.5500, 0.4500, and 0.6658 of the Radiology Department).
Conclusions: The model was constructed using a deep neural network and had high accuracy in LN localization and metastasis discrimination, which could contribute to accurate diagnosis and customized treatment planning.
Key points: • Lymph node metastasis is not well recognized with modern medical imaging tools. • Transfer learning can improve the accuracy of deep learning model prediction. • Deep learning can aid the accurate identification of lymph node metastasis.
Keywords: Deep learning; Diagnosis, computer-assisted; Lymphatic metastasis; Mouth neoplasms; Tomography, X-ray computed.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A deep learning and radiomics fusion model based on contrast-enhanced computer tomography improves preoperative identification of cervical lymph node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Dec 27;28(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05423-2. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 38151672
-
Segmentation of metastatic cervical lymph nodes from CT images of oral cancers using deep-learning technology.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2022 May 1;51(4):20210515. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20210515. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35113725 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-source dual-energy CT and deep learning for equivocal lymph nodes on CT images for thyroid cancer.Eur Radiol. 2024 Dec;34(12):7567-7579. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10854-w. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38904758
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast Enhanced Computed Tomography (CECT) in Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Oral Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Aug 1;25(8):2615-2623. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.8.2615. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39205558 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Cervical Cancer Lymph Node Metastasis via a Multimodal Transfer Learning Approach.Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2024 Oct 30;85(10):1-14. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2024.0428. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39475034 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiomics based on preoperative rectal cancer MRI to predict the metachronous liver metastasis.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023 Mar;48(3):833-843. doi: 10.1007/s00261-022-03773-1. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2023. PMID: 36529807
-
Assessing the Reporting Quality of Machine Learning Algorithms in Head and Neck Oncology.Laryngoscope. 2025 Feb;135(2):687-694. doi: 10.1002/lary.31756. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Laryngoscope. 2025. PMID: 39258420 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of convolutional neural network-based model to predict the risk of sentinel or non-sentinel lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer: a machine learning study.EClinicalMedicine. 2023 Aug 24;63:102176. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102176. eCollection 2023 Sep. EClinicalMedicine. 2023. PMID: 37662514 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Oral Cancer: A Comprehensive Scoping Review of Diagnostic and Prognostic Applications.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jan 24;15(3):280. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15030280. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A deep learning and radiomics fusion model based on contrast-enhanced computer tomography improves preoperative identification of cervical lymph node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Dec 27;28(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s00784-023-05423-2. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 38151672
References
-
- Pare A, Joly A. Oral cancer: risk factors and management. Presse Med. 2017;46:320–330. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

