Multicenter cohort study on duration of antiarrhythmic medication for supraventricular tachycardia in infants
- PMID: 36576576
- PMCID: PMC10023606
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-022-04757-5
Multicenter cohort study on duration of antiarrhythmic medication for supraventricular tachycardia in infants
Abstract
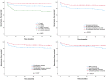
Antiarrhythmic medication (AM) is commonly used to prevent supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) recurrence in infants. Our aim was to determine whether a shorter duration of AM is sufficient to prevent atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT) recurrence and evaluate risk factors for recurrence of SVT after discontinued AM.This multicenter cohort study included all infants diagnosed with SVT in the five university hospitals in Finland between 2005 and 2017. Those diagnosed between 2005 and 2012 received AM for 12 months (group 1), and those diagnosed between 2013 and 2017 received AM for 6 months (group 2). A total of 278 infants presented with AVRT (group 1, n = 181; group 2, n = 97), and the median AM duration was 12.0 months (interquartile range [IQR] 11.4-13.4) and 7.0 months (IQR 6.0-10.2), respectively. Propranolol was the most frequently used first-line AM (92% and 95%). Recurrence-free survival rates were over 88% until 12 months after AM prophylaxis in both groups, without any statistically significant difference between them. Independent risk factors for recurrence of SVT after discontinuation of AM were need of combination AM (HR 2.2, 95% CI 1.14-4.20), Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome (HR 2.4, 95% CI 1.25-4.59), and age over 1 month at admission (HR 2.2, 95% CI 1.12-4.48). Conclusion: Shortening AM duration in infants from 12 to 6 months does not seem to lead to more frequent SVT recurrence. The risk factors for recurrence of SVT were WPW syndrome, need of combination AM, and age over 1 month.
Keywords: Antiarrhythmic medication; Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia; Infants; Prophylaxis; Supraventricular tachycardia.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Brugada J, Blom N, Sarquella-Brugada G, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Deanfield J, Janousek J, et al. Pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapy for arrhythmias in the pediatric population: EHRA and AEPC-Arrhythmia Working Group joint consensus statement. Europace. 2013;15:1337–1382. doi: 10.1093/europace/eut082. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nadas AS, Daeschner CW, Roth A, Blumenthal SL. Paroxysmal tachycardia in infants and children; study of 41 cases. Pediatr. 1952;9:167–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

