Child and adolescent food insecurity in South Africa: A household-level analysis of hunger
- PMID: 36576919
- PMCID: PMC9797094
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278191
Child and adolescent food insecurity in South Africa: A household-level analysis of hunger
Abstract
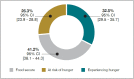
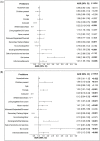
Food insecurity impacts childhood nutritional status, physical and cognitive development, and increases lifetime risk for chronic disease. Previous South African studies have examined hunger at the sub-national level without a specific focus on children and adolescents. This study determines the national prevalence of childhood food insecurity, from birth to adolescence, and identifies factors associated with hunger within the household. Individual and household-level data were extracted from the South African National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (SANHANES-1). Prevalence of food insecurity was assessed using the Community Childhood Hunger Identification Project (CCHIP) index. Multinomial logistic regression analyses were conducted on all households (with and without children) to determine the predictors of food insecurity, with additional analyses adjusting for child dependency and sociodemographic characteristics of household heads in households with children. Of 5 098 households surveyed, 68.6% had children and adolescents present (0-19 years). Of these households, 32.5% (95% Confidence Interval [CI]: 29.5-35.7) were experiencing hunger and 26.3% (95% CI: 23.9-28.8) were at risk of hunger. Among all the households, significant associations for experiencing hunger were the presence of children and adolescents: Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) = 1.68 (95% CI: 1.12-2.53); being female-headed: AOR = 1.53 (95% CI: 1.21-1.94) and informally-located; AOR = 1.6 (95% CI: 1.07-2.43). Of the racial groups, having a non-African household head, Coloured: AOR = 0.29 (95% CI: 0.19-0.44) and White/Indian/Asian: AOR = 0.12 (95% CI: 0.04-0.33) conferred lower odds of experiencing hunger; and, the household head having secondary/tertiary education conferred lower odds of experiencing hunger; AOR = 0.40 (95% CI: 0.28-0.56) as well as being at risk of hunger; AOR = 0.69 (95% CI: 0.52-0.92). Receiving social grants, pensions, or remittances more than doubled the odds of experiencing hunger; AOR = 2.15 (95% CI: 1.49-3.09). After adjusting for child dependency in households with children, having at least one older child (age 15-19 years old) did not change the odds of food insecurity. In summary, only 41% of South African households with children and adolescents were food secure. The associations between household head sociodemographics, household location and size on household food insecurity indicate a need for multi-sectoral interventions to bolster sustainable food systems for households with children and adolescents and to improve public protections for female-headed, African-headed and informally-located households dependent on social grants.
Copyright: © 2022 Mkhize et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights. Fact Sheet No. 34, The Right to Adequate Food [Internet]. Refworld. 2021 [cited 2021 Jun 7]. https://www.refworld.org/docid/4ca460b02.html.
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization. The Right to Food around the Globe [Internet]. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2015 [cited 2021 Jun 6]. http://www.fao.org/right-to-food-around-the-globe/countries/zaf/en/.
-
- Skoet J, Stamoulis KG. The state of food insecurity in the world 2006 [Internet]. Food and Agriculture Organization. 2006 [cited 2021 Jun 7]. http://www.fao.org/3/a0750e/a0750e00.pdf.
-
- Neuman N, Eli K, Nowicka P. Feeding the extended family: gender, generation, and socioeconomic disadvantage in food provision to children. Food, Cult Soc [Internet]. 2019; 22(1):45–62. 10.1080/15528014.2018.1547066. - DOI
-
- Fraval S, Hammond J, Bogard JR, Ng’endo M, van Etten J, Herrero M, et al.. Food access deficiencies in sub-Saharan Africa: prevalence and implications for agricultural interventions. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019. Nov 19; 3:104. 10.3389/fsufs.2019.00104. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

