The direct binding of Plasmodium vivax AMA1 to erythrocytes defines a RON2-independent invasion pathway
- PMID: 36577076
- PMCID: PMC9910450
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2215003120
The direct binding of Plasmodium vivax AMA1 to erythrocytes defines a RON2-independent invasion pathway
Abstract
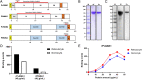
We used a transgenic parasite in which Plasmodium falciparum parasites were genetically modified to express Plasmodium vivax apical membrane antigen 1 (PvAMA1) protein in place of PfAMA1 to study PvAMA1-mediated invasion. In P. falciparum, AMA1 interaction with rhoptry neck protein 2 (RON2) is known to be crucial for invasion, and PfRON2 peptides (PfRON2p) blocked the invasion of PfAMA1 wild-type parasites. However, PfRON2p has no effect on the invasion of transgenic parasites expressing PvAMA1 indicating that PfRON2 had no role in the invasion of PvAMA1 transgenic parasites. Interestingly, PvRON2p blocked the invasion of PvAMA1 transgenic parasites in a dose-dependent manner. We found that recombinant PvAMA1 domains 1 and 2 (rPvAMA1) bound to reticulocytes and normocytes indicating that PvAMA1 directly interacts with erythrocytes during the invasion, and invasion blocking of PvRON2p may result from it interfering with PvAMA1 binding to erythrocytes. It was previously shown that the peptide containing Loop1a of PvAMA1 (PvAMA1 Loop1a) is also bound to reticulocytes. We found that the Loop1a peptide blocked the binding of PvAMA1 to erythrocytes. PvAMA1 Loop1a has no polymorphisms in contrast to other PvAMA1 loops and may be an attractive vaccine target. We thus present the evidence that PvAMA1 binds to erythrocytes in addition to interacting with PvRON2 suggesting that the P. vivax merozoites may exploit complex pathways during the invasion process.
Keywords: Plasmodium vivax; apical membrane antigen 1; transgenic parasites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

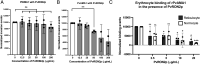

Similar articles
-
Structure of Rhoptry Neck Protein 2 is essential for the interaction in vitro with Apical Membrane Antigen 1 in Plasmodium vivax.Malar J. 2019 Jan 25;18(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2649-6. Malar J. 2019. PMID: 30683104 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-reactivity between apical membrane antgen 1 and rhoptry neck protein 2 in P. vivax and P. falciparum: A structural and binding study.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 17;12(8):e0183198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183198. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28817634 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Conservation of the AMA1 Host-Cell Invasion Ligand Between P. falciparum and P. vivax: A Novel Platform to Accelerate Vaccine and Drug Development.J Infect Dis. 2018 Jan 17;217(3):498-507. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix583. J Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29165651
-
Apical membrane antigen 1 as an anti-malarial drug target.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(16):2039-47. doi: 10.2174/156802611796575885. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21619512 Review.
-
Invasion of erythrocytes by malaria parasites: a cellular and molecular overview.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:451-77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.002315. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986. PMID: 3535649 Review.
Cited by
-
Complement receptor 1 is the human erythrocyte receptor for Plasmodium vivax erythrocyte binding protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jan 30;121(5):e2316304121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2316304121. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38261617 Free PMC article.
-
A broadly cross-reactive i-body to AMA1 potently inhibits blood and liver stages of Plasmodium parasites.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 22;15(1):7206. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50770-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39174515 Free PMC article.
-
State-of-the-art Review on the Antiparasitic Activity of Benzimidazolebased Derivatives: Facing Malaria, Leishmaniasis, and Trypanosomiasis.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(15):1955-1982. doi: 10.2174/0929867331666230915093928. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37718524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative analysis of codon usage patterns of Plasmodium helical interspersed subtelomeric (PHIST) proteins.Front Microbiol. 2023 Dec 14;14:1320060. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1320060. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38156001 Free PMC article.
-
Potent AMA1-specific human monoclonal antibody against Plasmodium vivax Pre-erythrocytic and Blood Stages.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 4;15(1):10556. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53848-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39632799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drew D. R., et al. , Functional conservation of the AMA1 host-cell invasion ligand between P. falciparum and P. vivax: A novel platform to accelerate vaccine and drug development. J. Infect. Dis. 217, 498–507 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Miller L. H., Mason S. J., Dvorak J. A., McGinniss M. H., Rothman I. K., Erythrocyte receptors for (Plasmodium knowlesi) malaria: Duffy blood group determinants. Science 189, 561–563 (1975). - PubMed
-
- Miller L. H., Mason S. J., Clyde D. F., McGinniss M. H., The resistance factor to Plasmodium vivax in blacks. The Duffy-blood-group genotype, FyFy. N. Engl. J. Med. 295, 302–304 (1976). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

