Responses of the tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa, Paeoniaceae) cultivar 'Yu Hong' to heat stress revealed by iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics
- PMID: 36578066
- PMCID: PMC9798725
- DOI: 10.1186/s12953-022-00202-5
Responses of the tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa, Paeoniaceae) cultivar 'Yu Hong' to heat stress revealed by iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics
Abstract
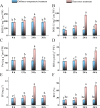
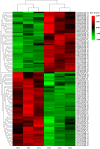
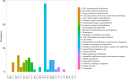
Horticulture productivity has been increasingly restricted by heat stress from growing global warming, making it far below the optimum production capacity. As a popular ornamental cultivar of tree peony, Paeonia suffruticosa 'Yu Hong' has also been suffering from heat stress not suitable for its optimal growth. To better understand the response mechanisms against heat stress of tree peony, investigations of phenotypic changes, physiological responses, and quantitative proteomics were conducted. Phenotypic and physiological changes indicated that 24 h of exposure to heat stress (40 °C) was the critical duration of heat stress in tree peony. The proteomic analyses revealed a total of 100 heat-responsive proteins (HRPs). According to bioinformatic analysis of HRPs, the heat tolerance of tree peony might be related to signal transduction, synthesis/degradation, heat kinetic proteins, antioxidants, photosynthesis, energy conversion, and metabolism. Our research will provide some new insights into the molecular mechanism under the response against the heat stress of tree peony, which will benefit the future breeding of heat-resistant ornamental plants.
Keywords: Abiotic stress; Heat-responsive proteins; Omics analyses; Ornamental plant; Physiological response.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



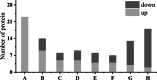
Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis of tree peony under high temperature treatment and functional verification of PsDREB2A gene.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025 Feb;219:109405. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.109405. Epub 2024 Dec 15. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39700913
-
Physiological and transcriptional responses to heat stress and functional analyses of PsHSPs in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa).Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 11;13:926900. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.926900. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36035676 Free PMC article.
-
Tolerance strategies revealed in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa; Paeoniaceae) ecotypes differentially adapted to desiccation.Appl Plant Sci. 2018 Oct 25;6(10):e01191. doi: 10.1002/aps3.1191. eCollection 2018 Oct. Appl Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30386716 Free PMC article.
-
Oil-use Feature of Tree Peony Seed Oil and Its Application in Functional Food Field.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Apr 17:e202500431. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202500431. Online ahead of print. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 40247429 Review.
-
[Heat-responsive mechanisms in plants revealed by proteomic analysis: A review].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2015 Aug;26(8):2561-70. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26685622 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the NAC gene family in 'Fengdan' peony (Paeonia ostii) insights into the evolution and expression patterns under abiotic stresses and ABA treatment.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Apr 16;16:1559667. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1559667. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40308307 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of the HSP20 Family in the Peony.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;16(7):742. doi: 10.3390/genes16070742. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40725398 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of NAC Gene Family Members of Tree Peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews) and Their Expression under Heat and Waterlogging Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 28;25(17):9312. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179312. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273263 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of High Temperature Stress on the Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Paeonia ostii.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 6;24(13):11180. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311180. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang YY, Xu L, Zhu XW, Gong YQ, Xiang F, Sun XC, Liu LW. Proteomic analysis of heat stress response in leaves of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) Plant Mol Biol Rep. 2013;31:195–203. doi: 10.1007/s11105-012-0486-7. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

