A fully automatic framework for evaluating cosmetic results of breast conserving therapy
- PMID: 36578375
- PMCID: PMC9794198
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mlwa.2022.100430
A fully automatic framework for evaluating cosmetic results of breast conserving therapy
Abstract
The breast cosmetic outcome after breast conserving therapy is essential for evaluating breast treatment and determining patient's remedy selection. This prompts the need of objective and efficient methods for breast cosmesis evaluations. However, current evaluation methods rely on ratings from a small group of physicians or semi-automated pipelines, making the processes time-consuming and their results inconsistent. To solve the problem, in this study, we proposed: 1. a fully-automatic Machine Learning Breast Cosmetic evaluation algorithm leveraging the state-of-the-art Deep Learning algorithms for breast detection and contour annotation, 2. a novel set of Breast Cosmesis features, 3. a new Breast Cosmetic dataset consisting 3k+ images from three clinical trials with human annotations on both breast components and their cosmesis scores. We show our fully-automatic framework can achieve comparable performance to state-of-the-art without the need of human inputs, leading to a more objective, low-cost and scalable solution for breast cosmetic evaluation in breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Breast Cosmesis scores; Breast cancer; Breast conserving therapy; Breast detection; Machine learning; Predictive model.
Figures

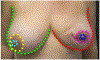
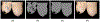
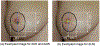
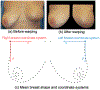
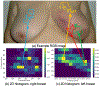
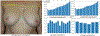
References
-
- Arjovsky M, Chintala S, & Bottou L (2017). Wasserstein GAN. arXiv:1701.07875.
-
- Brouwers P, Werkhoven E, Bartelink H, & Fourquet A (2016). Factors associated with patient-reported cosmetic outcome in the Young boost breast trial. Radiotherapy and Oncology. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso JS, & Cardoso MJ (2007). Towards an intelligent medical system for the aesthetic evaluation of breast cancer conservative treatment. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso MJ, Cardoso JS, Wild T, Krois W, & Fitzal F (2009). Comparing two objective methods for the aesthetic evaluation of breast cancer conservative treatment. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
