Identification of DOT1L inhibitor in a screen for factors that promote dopaminergic neuron survival
- PMID: 36578445
- PMCID: PMC9791259
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1026468
Identification of DOT1L inhibitor in a screen for factors that promote dopaminergic neuron survival
Abstract
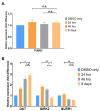
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra region of the midbrain. Diagnostic criteria for PD require that at least two of three motor signs are observed: tremor, rigidity, and/or bradykinesia. The most common and effective treatment for PD is Levodopa (L-DOPA) which is readily converted to DA and has been the primary treatment since the 1960's. Dopamine agonists have also been developed but are less effective than L-DOPA. Although the lack of a model system to study PD has hampered efforts to identify treatments, diverse screening strategies have been proposed for identification of new pharmaceutical candidates. Here, we describe a pilot screen to identify candidate molecules from a bioactive compound library, that might increase formation, maintenance and/or survival of DA neurons in vitro. The screen used a previously characterized reporter construct consisting of the luciferase gene inserted downstream of the endogenous tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) gene and neurons differentiated from human pluripotent stem cells for 18 days. The reporter mimics expression of TH and includes a secreted luciferase whose activity can be measured non-invasively over multiple timepoints. Screening of the bioactive compound library resulted in the identification of a single molecule, SGC0946, that is an inhibitor of DOT1L (Disruptor Of Telomeric silencing 1-Like) which encodes a widely-conserved histone H3K79 methyltransferase that is able to both activate and repress gene transcription. Our results indicate that SGC0946 increased reporter luciferase activity with a single treatment for 48-h post-plating being equivalent to continuous treatment. Moreover, data suggested that the total number of neurons differentiated in the assays was comparable from experiment to experiment under different SGC0946 treatments over time. In contrast, data suggested that the survival and/or maintenance of DA neurons might be specifically enhanced by SGC0946 treatment. These results document the feasibility of a set of tools for further exploration of small molecules that may impact DA neuron differentiation, maintenance and/or survival. Results provide evidence in support of other reports that indicate inhibition of DOT1L may play an important role in maintenance and survival of neural progenitor cells (NPCs) and their lineage-specific differentiation.
Keywords: DOT1L; DOT1L inhibition; Parkinson’s disease; SGC0946; dopaminergic neuron; high throughput screen; human pluripotent stem cell; neural progenitor cells.
Copyright © 2022 Cui, Carey and Reijo Pera.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Barbuti P., Antony P., Santos B., Massart F., Cruciani G., Dording C., et al. (2020). Using high-content screening to generate single-cell gene-corrected patient-derived ips clones reveals excess alpha-synuclein with familial Parkinson’s disease point mutation A30P. Cells 9:2065. doi: 10.3390/cells9092065, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

