Diagnosis and Emerging Treatment Strategies for Mucopolysaccharidosis VII (Sly Syndrome)
- PMID: 36578769
- PMCID: PMC9791935
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S351300
Diagnosis and Emerging Treatment Strategies for Mucopolysaccharidosis VII (Sly Syndrome)
Abstract
Mucopolysaccharidosis VII (MPS VII, Sly syndrome) is an ultra-rare lysosomal disease caused by a deficiency of the enzyme β-glucuronidase (GUS). The diagnosis is suspected based on a range of symptoms that are common to many other MPS types, and it is confirmed through biochemical and molecular studies. Besides supportive treatment, current and emerging treatments include enzyme replacement therapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and gene therapy. This review summarizes the clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and emerging treatments for MPS VII.
Keywords: Sly syndrome; enzyme replacement therapy; gene therapy; hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; lysosomal disorders; mucopolysaccharidosis type VII.
© 2022 Poswar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures
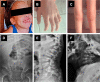
Similar articles
-
Mucopolysaccharidosis type VII (Sly syndrome) - What do we know?Mol Genet Metab. 2024 Mar;141(3):108145. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2024.108145. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Mol Genet Metab. 2024. PMID: 38301529 Review.
-
Lentiviral-mediated gene therapy results in sustained expression of β-glucuronidase for up to 12 months in the gus(mps/mps) and up to 18 months in the gus(tm(L175F)Sly) mouse models of mucopolysaccharidosis type VII.Hum Gene Ther. 2014 Sep;25(9):798-810. doi: 10.1089/hum.2013.141. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Hum Gene Ther. 2014. PMID: 25003807
-
Missense models [Gustm(E536A)Sly, Gustm(E536Q)Sly, and Gustm(L175F)Sly] of murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII produced by targeted mutagenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Nov 12;99(23):14982-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.232570999. Epub 2002 Oct 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12403825 Free PMC article.
-
Murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII: the impact of therapies on the clinical course and pathology in a murine model of lysosomal storage disease.J Inherit Metab Dis. 1998 Aug;21(5):575-86. doi: 10.1023/a:1005423222927. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1998. PMID: 9728337 Review.
-
Clinical course of sly syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type VII).J Med Genet. 2016 Jun;53(6):403-18. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103322. Epub 2016 Feb 23. J Med Genet. 2016. PMID: 26908836 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prenatal Delivery of Enzyme Replacement Therapy to Fetuses Affected by Early-Onset Lysosomal Storage Diseases.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2025 Jan 31:e32132. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.32132. Online ahead of print. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2025. PMID: 39891377 Review.
-
Metabolic Cardiomyopathies and Cardiac Defects in Inherited Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 11;24(10):8632. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108632. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239976 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Seeking into Cell-Free Therapies for Bone-Affected Lysosomal Storage Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 4;26(13):6448. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136448. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A de novo homozygous missense mutation of the GUSB gene leads to mucopolysaccharidosis type VII identification in a family with twice adverse pregnancy outcomes due to non-immune hydrops fetalis.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2023 Dec 6;38:101033. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2023.101033. eCollection 2024 Mar. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2023. PMID: 38149215 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Diseases and Rare Disorders: Is It a Lysosomal Storage Disease? Differential Diagnosis, Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Management.Children (Basel). 2024 May 30;11(6):668. doi: 10.3390/children11060668. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929247 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Neufeld EF, Muenzer J. The mucopolysaccharidoses. In: Valle DL, Antonarakis S, Ballabio A, Beaudet AL, Michell GA, editors. The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. McGraw Hill; 2007.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

