Challenges in treatment of patients with non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- PMID: 36578966
- PMCID: PMC9791115
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1064024
Challenges in treatment of patients with non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Abstract
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) due to 21α-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD) or 11β-hydroxylase deficiency (11OHD) are congenital conditions with affected adrenal steroidogenesis. Patients with classic 21OHD and 11OHD have a (nearly) complete enzyme deficiency resulting in impaired cortisol synthesis. Elevated precursor steroids are shunted into the unaffected adrenal androgen synthesis pathway leading to elevated adrenal androgen concentrations in these patients. Classic patients are treated with glucocorticoid substitution to compensate for the low cortisol levels and to decrease elevated adrenal androgens levels via negative feedback on the pituitary gland. On the contrary, non-classic CAH (NCCAH) patients have more residual enzymatic activity and do generally not suffer from clinically relevant glucocorticoid deficiency. However, these patients may develop symptoms due to elevated adrenal androgen levels, which are most often less elevated compared to classic patients. Although glucocorticoid treatment can lower adrenal androgen production, the supraphysiological dosages also may have a negative impact on the cardiovascular system and bone health. Therefore, the benefit of glucocorticoid treatment is questionable. An individualized treatment plan is desirable as patients can present with various symptoms or may be asymptomatic. In this review, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of different treatment options used in patients with NCCAH due to 21OHD and 11OHD.
Keywords: 11-hydroxylase deficiency (11OHD); 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD); Non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia (NCCAH); glucocorticoid treatment; treatment options.
Copyright © 2022 Adriaansen, Schröder, Span, Sweep, van Herwaarden and Claahsen-van der Grinten.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
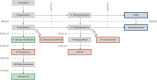
Figures

References
-
- Krone N, Rose IT, Willis DS, Hodson J, Wild SH, Doherty EJ, et al. . Genotype-phenotype correlation in 153 adult patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: Analysis of the united kingdom congenital adrenal hyperplasia adult study executive (CaHASE) cohort. J Clin Endocrinol Metab (2013) 98(2):E346–54. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-3343 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

