Invasive Pneumococcal Disease and COVID-19 Coinfection: A Series of Cases Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit
- PMID: 36579230
- PMCID: PMC9790083
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.31876
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease and COVID-19 Coinfection: A Series of Cases Admitted to an Intensive Care Unit
Abstract
Pneumococcal infection is still a frequent disease. It can be classified as invasive when pneumococcus is isolated in a generally sterile fluid. Pneumonia is the most common infectious source of adult invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD), and several risk factors for IPD are well known. This case report presents three clinical cases of different manifestations of IPD. The two most severe cases had coinfection by SARS-CoV-2 at hospital admission.
Keywords: invasive pneumococcal disease; pneumonia; risk factors; sars-cov-2; streptococcus pneumoniae.
Copyright © 2022, Almeida et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
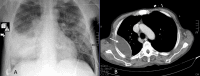
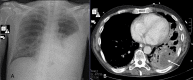
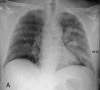
Similar articles
-
Impact of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic on Invasive Pneumococcal Disease and Risk of Pneumococcal Coinfection With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Prospective National Cohort Study, England.Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Mar 1;72(5):e65-e75. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1728. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33196783 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive pneumococcal disease burden in hospitalized adults in Bogota, Colombia.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Oct 12;21(1):1059. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06769-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34641809 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial and fungal coinfection among hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study in a UK secondary-care setting.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Oct;26(10):1395-1399. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.06.025. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32603803 Free PMC article.
-
[Thousand faces of Streptococcus pneumonia (pneumococcus) infections].Orv Hetil. 2015 Nov 1;156(44):1769-77. doi: 10.1556/650.2015.30293. Orv Hetil. 2015. PMID: 26498896 Review. Hungarian.
-
Asthma and the Risk of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease: A Meta-analysis.Pediatrics. 2020 Jan;145(1):e20191200. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-1200. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Pediatrics. 2020. PMID: 31843863 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 and Streptococcus pneumoniae colonization and disease: an observational study in adults.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jul 18;15:1624521. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1624521. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40756030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Vol. 5. Stockholm: 2020. Invasive pneumococcal disease. Annual epidemiological report for 2018; p. 2022.
-
- Streptococcus pneumoniae antigen in urine: diagnostic usefulness and impact on outcome of bacteraemic pneumococcal pneumonia in a large series of adult patients. Zalacain R, Capelastegui A, Ruiz LA, Bilbao A, Gomez A, Uranga A, España PP. Respirology. 2014;19:936–943. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
