Assessment of hOGG1 Genetic Polymorphism (rs1052133) and DNA Damage in Radiation-Exposed Workers
- PMID: 36579980
- PMCID: PMC9971479
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.12.4005
Assessment of hOGG1 Genetic Polymorphism (rs1052133) and DNA Damage in Radiation-Exposed Workers
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the effect of radiation exposure, human 8-oxoguanine DNA N-glycosylase-1 (hOGG1) exon 7 genetic polymorphism and confounding factors on DNA damage response.
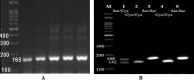
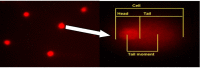
Methods: Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) and alkaline Comet assay method were applied to determine the hOGG1 genetic polymorphisms and DNA damage response. A total of 80 participants were enrolled in this study, consisting of 40 radiation-exposed workers as a case group and 40 non-radiation workers as a control group.
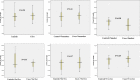
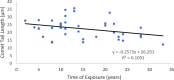
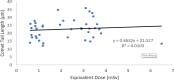
Result: The genotypes frequencies for controls were Ser/Ser (35%), Ser/Cys (32.5%), and Cys/Cys (32.5%), with frequencies of alleles being 326Ser (0.52) and 326Cys (0.48), whereas the genotypes frequencies for radiation-exposed workers (cases group) were Ser/Ser (17.5%), Ser/Cys (57.5%), and Cys/Cys (25%), with frequencies of alleles being 326Ser (0.46) and 326Cys (0.54). The results indicated that DNA damage response were not significantly higher in the exposed workers than in controls (22.55 ± 6.02 versus 21.72 ± 7.14; P=0.58). The time of exposure has a significantly negative correlation with comet tail length value among radiation workers. In addition, it was found that the DNA damage response was strongly associated with age and time of exposure with a decrease of 0.6 percent (P-value: 0.008) and 0.58 percent (P-value: 0.009), respectively. Whereas gender, smoking habit, and equivalent dose were not correlated with DNA damage.
Conclusion: The single-nucleotide polymorphism of hOGG1 exon 7 (rs1052133) demonstrated no association with the extent of DNA damage in radiation-exposed workers.
Keywords: Alkaline comet assay; DNA damage; Genetic polymorphism; Radiation-exposed workers; hOGG1 exon 7.
Figures
References
-
- Alanazi M, Pathan AAK, Shaik JP, et al. The hOGG1 Ser326Cys gene polymorphism and breast cancer risk in Saudi population. Pathol Oncol Res. 2017;23:525–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

