Computational analysis of synergism in small networks with different logic
- PMID: 36580168
- PMCID: PMC9958226
- DOI: 10.1007/s10867-022-09620-0
Computational analysis of synergism in small networks with different logic
Abstract
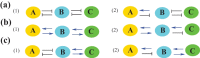
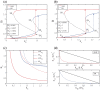
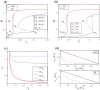
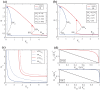
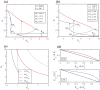
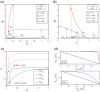
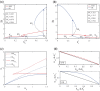
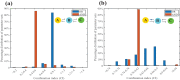
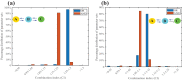
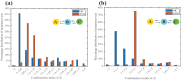
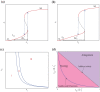
Cell fate decision processes are regulated by networks which contain different molecules and interactions. Different network topologies may exhibit synergistic or antagonistic effects on cellular functions. Here, we analyze six most common small networks with regulatory logic AND or OR, trying to clarify the relationship between network topologies and synergism (or antagonism) related to cell fate decisions. We systematically examine the contribution of both network topologies and regulatory logic to the cell fate synergism by bifurcation and combinatorial perturbation analysis. Initially, under a single set of parameters, the synergism of three types of networks with AND and OR logic is compared. Furthermore, to consider whether these results depend on the choices of parameter values, statistics on the synergism of five hundred parameter sets is performed. It is shown that the results are not sensitive to parameter variations, indicating that the synergy or antagonism mainly depends on the network topologies rather than the choices of parameter values. The results indicate that the topology with "Dual Inhibition" shows good synergism, while the topology with "Dual Promotion" or "Hybrid" shows antagonism. The results presented here may help us to design synergistic networks based on network structure and regulation combinations, which has promising implications for cell fate decisions and drug combinations.
Keywords: Cell fate decisions; Logic gates; Network topologies; Synergism.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

