Coal dust nanoparticles induced pulmonary fibrosis by promoting inflammation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway driven by IGF1/ROS-mediated AKT/GSK3β signals
- PMID: 36581638
- PMCID: PMC9800584
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-01291-z
Coal dust nanoparticles induced pulmonary fibrosis by promoting inflammation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway driven by IGF1/ROS-mediated AKT/GSK3β signals
Abstract
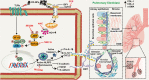
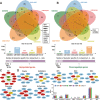
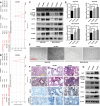
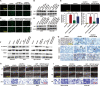
Pneumoconiosis is the most common and serious disease among coal miners. In earlier work on this subject, we documented that coal dust (CD) nanoparticles (CD-NPs) induced pulmonary fibrosis (PF) more profoundly than did CD micron particles (CD-MPs), but the mechanism has not been thoroughly studied. Based on the GEO database, jveen, STRING, and Cytoscape tools were used to screen hub genes regulating PF. Particle size distribution of CD were analyzed with Malvern nanoparticle size potentiometer. Combining 8 computational methods, we found that IGF1, POSTN, MMP7, ASPN, and CXCL14 may act as hub genes regulating PF. Based on the high score of IGF1 and its important regulatory role in various tissue fibrosis, we selected it as the target gene in this study. Activation of the IGF1/IGF1R axis promoted CD-NPs-induced PF, and inhibition of the axis activation had the opposite effect in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, activation of the IGF1/IGF1R axis induced generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) to accelerate PF. High-throughput gene sequencing based on lung tissue suggested that cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction and the NF-kB signaling pathway play a key role in PF. Also, ROS induced inflammation and EMT by the activation of the NF-kB/NLRP3 axis to accelerate PF. ROS can induce the activation of AKT/GSK3β signaling, and inhibition of it can inhibit ROS-induced inflammation and EMT by the NF-kB/NLRP3 axis, thereby inhibiting PF. CD-NPs induced PF by promoting inflammation and EMT via the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway driven by IGF1/ROS-mediated AKT/GSK3β signals. This study provides a valuable experimental basis for the prevention and treatment of coal workers' pneumoconiosis. Illustration of the overall research idea of this study: IGF1 stimulates coal dust nanoparticles induced pulmonary fibrosis by promoting inflammation and EMT via the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway driven by ROS-mediated AKT/GSK3β signals.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differences in the characteristics and pulmonary toxicity of nano- and micron-sized respirable coal dust.Respir Res. 2022 Jul 30;23(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02120-8. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 35906696 Free PMC article.
-
Calycosin attenuates pulmonary fibrosis by the epithelial-mesenchymal transition repression upon inhibiting the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway.Acta Histochem. 2021 Jul;123(5):151746. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2021.151746. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Acta Histochem. 2021. PMID: 34217047
-
Reactive oxygen species trigger NF-κB-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles in A549 cells.Toxicol Ind Health. 2017 Oct;33(10):737-745. doi: 10.1177/0748233717712409. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Toxicol Ind Health. 2017. PMID: 28870124
-
The Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Process During the Fibrosis.Front Immunol. 2020 May 20;11:883. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00883. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32508821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond the pill: incrimination of nuclear factor-kappa B and their targeted phytomedicine for pulmonary fibrosis.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 26. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04067-1. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40137966 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive drug delivery systems for photodynamic therapy of cancer.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Dec;14(12):5106-5131. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.10.015. Epub 2024 Nov 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39807318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MSC-derived exosome ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by modulating NOD 1/NLRP3-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inflammation.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 26;11(2):e41436. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41436. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39872463 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal Manf originated from endothelium regulated osteoclast differentiation by down-regulating NF-κB signaling pathway.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Apr 7;20(1):349. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05671-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40197525 Free PMC article.
-
Triptolide Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis and Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats by Suppressing IGF1-Mediated Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 May 26. doi: 10.1007/s11655-025-4224-z. Online ahead of print. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 40418457
-
Unraveling the potential of vitamins C and D as adjuvants in depression treatment with escitalopram in an LPS animal model.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Apr;32(2):1147-1157. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01404-9. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38180676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Energy Agency (EIA). Coal information: 2017, Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Publishing, Paris, 10.1787/coal-2017-en. 2017.
-
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. Short-term energy outlook (STEO), Energy Information Administration, U.S., https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/steo/analysis.php. 2018;2.
-
- Zou XX, Zhang B, Wang HJ. [Study on the current situation of social security for pneumoconiosis in China] Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2021;39:954–6. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

