Targeting SOST using a small-molecule compound retards breast cancer bone metastasis
- PMID: 36581888
- PMCID: PMC9798707
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01697-4
Targeting SOST using a small-molecule compound retards breast cancer bone metastasis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Targeting SOST using a small‑molecule compound retards breast cancer bone metastasis.Mol Cancer. 2025 Apr 16;24(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02322-w. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40241133 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer metastasis to the bone can be exacerbated by osteoporosis, is associated with poor long-term survival, and has limited therapeutic options. Sclerostin (SOST) is an endogenous inhibitor of bone formation, and an attractive target for treatment of osteoporosis. However, it is unclear whether SOST can be used as a therapeutic target for bone metastases of breast cancer, and whether small molecule compounds that target SOST in breast cancer cells can inhibit breast cancer bone metastasis.
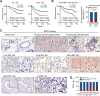
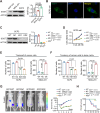
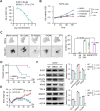
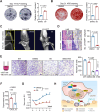
Methods: SOST expression in 442 breast cancer tissues was characterized by immunohistochemistry and statistically analyzed for the association with breast cancer bone metastases. Bone metastatic breast cancer SCP2 cells were induced for SOST silencing or overexpression and their bone metastatic behaviors were tested in vitro and in vivo. To identify potential therapeutics, we screened inhibitors of the interaction of SOST with STAT3 from a small chemical molecule library and tested the inhibitory effects of one inhibitor on breast cancer growth and bone metastasis in vitro and in vivo.
Results: We found that up-regulated SOST expression was associated with breast cancer bone metastases and worse survival of breast cancer patients. SOST silencing significantly reduced the bone metastatic capacity of SCP2 cells. SOST interacted with STAT3 to enhance the TGF-β/KRAS signaling, increasing both tumor growth and bone metastasis. Treatment with one lead candidate, S6, significantly inhibited the growth of breast-cancer organoids and bone metastasis in mice.
Conclusions: Our findings highlight a new class of potential therapeutics for treatment of bone metastasis in breast cancer.
Keywords: Bone metastasis; Breast cancer; SOST; Small-molecule compound.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Friedl TWP, Fehm T, Muller V, Lichtenegger W, Blohmer J, Lorenz R, Forstbauer H, Fink V, Bekes I, Huober J, et al. Prognosis of patients with early breast cancer receiving 5 years vs 2 years of adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7:1149–57. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fromigue O, Lagneaux L, Body JJ. Bisphosphonates induce breast cancer cell death in vitro. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15:2211–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

