Targeting hyaluronic acid synthase-3 (HAS3) for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 36581895
- PMCID: PMC9801563
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-022-02818-1
Targeting hyaluronic acid synthase-3 (HAS3) for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hyaluronic acid (HA) promotes cancer metastasis; however, the currently approved treatments do not target HA. Metastatic renal carcinoma (mRCC) is an incurable disease. Sorafenib (SF) is a modestly effective antiangiogenic drug for mRCC. Although only endothelial cells express known SF targets, SF is cytotoxic to RCC cells at concentrations higher than the pharmacological-dose (5-µM). Using patient cohorts, mRCC models, and SF combination with 4-methylumbelliferone (MU), we discovered an SF target in RCC cells and targeted it for treatment.
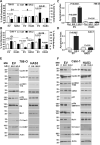
Methods: We analyzed HA-synthase (HAS1, HAS2, HAS3) expression in RCC cells and clinical (n = 129), TCGA-KIRC (n = 542), and TCGA-KIRP (n = 291) cohorts. We evaluated the efficacy of SF and SF plus MU combination in RCC cells, HAS3-transfectants, endothelial-RCC co-cultures, and xenografts.
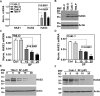
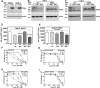
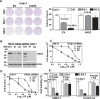
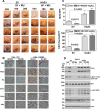
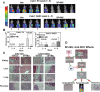
Results: RCC cells showed increased HAS3 expression. In the clinical and TCGA-KIRC/TCGA-KIRP cohorts, higher HAS3 levels predicted metastasis and shorter survival. At > 10-µM dose, SF inhibited HAS3/HA-synthesis and RCC cell growth. However, at ≤ 5-µM dose SF in combination with MU inhibited HAS3/HA synthesis, growth of RCC cells and endothelial-RCC co-cultures, and induced apoptosis. The combination inhibited motility/invasion and an HA-signaling-related invasive-signature. We previously showed that MU inhibits SF inactivation in RCC cells. While HAS3-knockdown transfectants were sensitive to SF, ectopic-HAS3-expression induced resistance to the combination. In RCC models, the combination inhibited tumor growth and metastasis with little toxicity; however, ectopic-HAS3-expressing tumors were resistant.
Conclusion: HAS3 is the first known target of SF in RCC cells. In combination with MU (human equivalent-dose, 0.6-1.1-g/day), SF targets HAS3 and effectively abrogates mRCC.
Keywords: 4-methylumbelliferone; HAS3; Hyaluronic acid; Molecular targeting; Renal cell carcinoma; Sorafenib.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abu-Ghanem Y, Fernandez-Pello S, Bex A, Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Dabestani S, Giles RH, Hofmann F, Hora M, Kuczyk MA, et al. Limitations of available studies prevent reliable comparison between tumour ablation and partial nephrectomy for patients with localised renal masses: a systematic review from the European association of urology renal cell cancer guideline panel. Eur Urol Oncol. 2020;3:433–452. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2020.02.001. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

