Dynamic changes of CSF clusterin levels across the Alzheimer's disease continuum
- PMID: 36581903
- PMCID: PMC9801612
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-022-03038-w
Dynamic changes of CSF clusterin levels across the Alzheimer's disease continuum
Abstract
Background: Clusterin is a multifunctional protein, which is associated with the pathogenesis and the development of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Compared with normal controls, inconsistent results have yielded in previous studies for concentration of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) clusterin in AD patients. We explored CSF clusterin levels in different pathological processes of AD.
Methods: Following the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association (NIA-AA) criteria, we employed on the levels of CSF Aβ42(A), phosphorylated-Tau (T), and total-tau (N). Based on previously published cutoffs and the close correlation between CSF p-tau and t-tau, 276 participants from the publicly available ADNI database with CSF biomarkers were divided into four groups: A-(TN)- (normal Aβ42 and normal p-tau and t-tau; n = 50), A+(TN)- (abnormal Aβ42 and normal p-tau and t-tau; n = 39), A+(TN) + (abnormal Aβ42 and abnormal p-tau or t-tau; n = 147), A-(TN) + (normal Aβ42 and abnormal p-tau or t-tau; n = 40). To assess CSF clusterin levels in AD continuum, intergroup differences in four groups were compared. Pairwise comparisons were conducted as appropriate followed by Bonferroni post hoc analyses. To further study the relationships between CSF clusterin levels and AD core pathological biomarkers, we employed multiple linear regression method in subgroups.
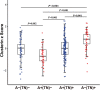
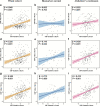
Results: Compared with the A-(TN)- group, CSF clusterin levels were decreased in A+ (TN)- group (P = 0.002 after Bonferroni correction), but increased in the A+(TN) + group and the A-(TN) + group (both P < 0.001 after Bonferroni correction). Moreover, we found CSF clusterin levels are positively associated with CSF Aβ42 (β = 0.040, P < 0. 001), CSF p-tau (β = 0.325, P < 0.001) and CSF t-tau (β = 0.346, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Our results indicated that there are differences levels of CSF clusterin in different stages of AD pathology. The CSF clusterin level decreased at the early stage are related to abnormal Aβ pathology; and the increased levels are associated with tau pathology and neurodegeneration.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ; CSF; Clusterin; Neurodegeneration; Tau.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Longitudinal structural cerebral changes related to core CSF biomarkers in preclinical Alzheimer's disease: A study of two independent datasets.Neuroimage Clin. 2018 Apr 16;19:190-201. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.04.016. eCollection 2018. Neuroimage Clin. 2018. PMID: 30023169 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid β2-microglobulin promotes the tau pathology through microglia-astrocyte communication in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Jan 2;17(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01665-8. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39748415 Free PMC article.
-
Glial activation and inflammation along the Alzheimer's disease continuum.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Feb 21;16(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1399-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 30791945 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous analysis of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers using microsphere-based xMAP multiplex technology for early detection of Alzheimer's disease.Methods. 2012 Apr;56(4):484-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.03.023. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Methods. 2012. PMID: 22503777 Review.
-
The Role of CSF Transthyretin in Human Alzheimer's Disease: Offense, Defense, or not so Innocent Bystander.J Integr Neurosci. 2023 Nov 6;22(6):158. doi: 10.31083/j.jin2206158. J Integr Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38176942 Review.
Cited by
-
The clusterin connectome: Emerging players in chondrocyte biology and putative exploratory biomarkers of osteoarthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 15;14:1103097. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1103097. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37033956 Free PMC article.
-
Motor, affective, cognitive, and perceptual symptom changes over time in individuals with Parkinson's disease who develop freezing of gait.J Neurol. 2025 Apr 8;272(5):321. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-13034-y. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40198411
-
Coupling of Alzheimer's Disease Genetic Risk Factors with Viral Susceptibility and Inflammation.Aging Dis. 2024 Oct 1;15(5):2028-2050. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.1017. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 37962454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexual dimorphisms in innate immune activation markers in predementia Alzheimer's disease.Brain Commun. 2025 Apr 25;7(3):fcaf161. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaf161. eCollection 2025. Brain Commun. 2025. PMID: 40322776 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the intersection of atherosclerosis and Alzheimer's disease: the role of inflammation and complement activation.Inflamm Res. 2025 Jul 10;74(1):102. doi: 10.1007/s00011-025-02069-6. Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40637922 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

