Soluble CD146 in the detection and grading of intravascular and tissue congestion in patients with acute dyspnoea: analysis of the prospective observational Lithuanian Echocardiography Study of Dyspnoea in Acute Settings (LEDA) cohort
- PMID: 36581965
- PMCID: PMC9438196
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-061611
Soluble CD146 in the detection and grading of intravascular and tissue congestion in patients with acute dyspnoea: analysis of the prospective observational Lithuanian Echocardiography Study of Dyspnoea in Acute Settings (LEDA) cohort
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the potential of soluble cluster of differentiation 146 (sCD146) in the detection and grading of congestion in patients with acute dyspnoea.
Design: Subanalysis of the prospective observational Lithuanian Echocardiography Study of Dyspnoea in Acute Settings (LEDA) cohort.
Setting: Two Lithuanian university centres.
Participants: Adult patients with acute dyspnoea admitted to the emergency department.
Methods: Congestion was assessed using clinical and sonographic parameters. All patients underwent sCD146 and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) testing.
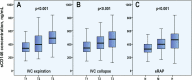
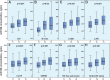
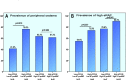
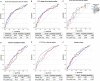
Results: The median value of sCD146 concentration in the study cohort (n=437) was 405 (IQR 315-509) ng/mL. sCD146 was higher in patients with peripheral oedema than in those without (median (IQR) 472 (373-535) vs 400 (304-501) ng/mL, p=0.009) and with pulmonary rales than in those without (439 (335-528) vs 394 (296-484) ng/mL, p=0.001). We found a parallel increase of estimated right atrial pressure (eRAP) and sCD146 concentration: sCD146 was 337 (300-425), 404 (290-489) and 477 (363-572) ng/mL in patients with normal, moderately elevated and high eRAP, respectively (p=0.001). In patients with low NT-proBNP, high sCD146 distinguished a subgroup with a higher prevalence of oedema as compared with patients with low levels of both biomarkers (76.0% vs 41.0%, p=0.010). Moreover, high sCD146 indicated a higher prevalence of elevated eRAP, irrespective of NT-proBNP concentration (p<0.05).
Conclusion: sCD146 concentration reflects the degree of intravascular and tissue congestion assessed by clinical and echocardiographic indices, with this association maintained in patients with low NT-proBNP. Our data support the notion that NT-proBNP might represent heart stretch while sCD146 rather represents peripheral venous congestion.
Keywords: Adult cardiology; Echocardiography; Heart failure; Ultrasound; VASCULAR MEDICINE.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AM received speaker’s honoraria from Orion, Otsuka, Philips, Roche and Servier; received fee as a member of advisory board and/or Steering Committee and/or research grant from Adrenomed, Epygon, Neurotronik, Roche, Sanofi and Sphyngotec. AM owns shares in S-Form Pharma. AK received speaker’s honoraria from Servier, Bayer, Berlin-Chemie-Menarini, Pfizer and KRKA. JČ received investigator and speaker fees from Sanofi, Amgen, Novartis, Roche Diagnostics, Servier, AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim. DŽ received speaker fees from Novartis and AstraZeneca. JS received personal fees from Novartis, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim and Servier. VJ received personal fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Servier and Pfizer. Other authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Soluble CD146, a new endothelial biomarker of acutely decompensated heart failure.Int J Cardiol. 2015 Nov 15;199:241-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.07.039. Epub 2015 Jul 12. Int J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26209827
-
Soluble CD146 Is a Novel Marker of Systemic Congestion in Heart Failure Patients: An Experimental Mechanistic and Transcardiac Clinical Study.Clin Chem. 2017 Jan;63(1):386-393. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.260471. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Clin Chem. 2017. PMID: 28062630 Clinical Trial.
-
Pro-brain natriuretic peptide plasma levels, left ventricular dimensions and ejection fraction in acute dyspnoea.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2012 Dec;22(12):751-5. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2012. PMID: 23217478
-
Use of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) and N-Terminal proBNP (NT-proBNP) as Diagnostic Tests in Adults With Suspected Heart Failure: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2021 May 6;21(2):1-125. eCollection 2021. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2021. PMID: 34055110 Free PMC article.
-
Amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide testing and prognosis in patients with acute dyspnea, including those with acute heart failure.Am J Cardiol. 2008 Feb 4;101(3A):49-55. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.11.020. Am J Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18243859 Review.
Cited by
-
The Congestion "Pandemic" in Acute Heart Failure Patients.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 24;12(5):951. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12050951. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38790913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble CD146 in Heart Failure: Pathophysiological Role and Diagnostic Potential.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 3;13(6):1370. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061370. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564089 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
