Association between prenatal maternal anxiety and/or stress and offspring's cognitive functioning: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36582056
- PMCID: PMC10952806
- DOI: 10.1111/cdev.13885
Association between prenatal maternal anxiety and/or stress and offspring's cognitive functioning: A meta-analysis
Abstract
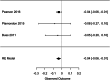
This meta-analysis examined the relationship between prenatal maternal stress and/or anxiety and the outcomes of children aged 3 months to 9 years. Of the 8754 studies published before June 2021 that were synthesized, 17 conducted in Western countries were included in the meta-analysis (Ntotal = 23,307; Mmales 54%; Methnicity White 77%, Pacific 15%, African American/Black 10%, Middle Eastern 7%, Eastern 8%). Effect sizes ranged from -0.41 to 0.15. A weak negative association was found between prenatal stress and/or anxiety exposure and children's general intellectual development. Associations varied based on the type of exposure. Findings are limited to developed counties and cannot be generalized to low- and middle-income countries. Directions for maternal prenatal intervention and future studies are discussed.
© 2022 The Authors. Child Development published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Society for Research in Child Development.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson, V. A. , Anderson, P. , Northam, E. , Jacobs, R. , & Mikiewicz, O. (2002). Relationships between cognitive and behavioral measures of executive function in children with brain disease. Child Neuropsychology, 8(4), 231–240. - PubMed
-
- Anger, S. , & Heineck, G. (2010). Do smart parents raise smart children? The intergenerational transmission of cognitive abilities. Journal of Population Economics, 23(3), 1105–1132.
-
- Appleyard, K. , Egeland, B. , van Dulmen, M. H. , & Alan Sroufe, L. (2005). When more is not better: The role of cumulative risk in child behavior outcomes. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 46(3), 235–245. - PubMed
-
- Austin, M. P. , Christl, B. , McMahon, C. , Kildea, S. , Reilly, N. , Yin, C. , Simcock, G. , Elgbeili, G. , Laplante, D. , & King, S. (2017). Moderating effects of maternal emotional availability on language and cognitive development in toddlers of mothers exposed to a natural disaster in pregnancy: The QF2011 Queensland Flood Study. Infant Behavior and Development, 49, 296–309. - PubMed

