Steroid receptor coactivators - their role in immunity
- PMID: 36582250
- PMCID: PMC9793089
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1079011
Steroid receptor coactivators - their role in immunity
Abstract
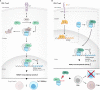
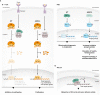
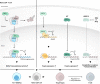
Steroid Receptor Coactivators (SRCs) are essential regulators of transcription with a wide range of impact on human physiology and pathology. In immunology, SRCs play multiple roles; they are involved in the regulation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), macrophage (MΦ) activity, lymphoid cells proliferation, development and function, to name just a few. The three SRC family members, SRC-1, SRC-2 and SRC-3, can exert their immunological function either in an independent manner or act in synergy with each other. In certain biological contexts, one SRC family member can compensate for lack of activity of another member, while in other cases one SRC can exert a biological function that competes against the function of another family counterpart. In this review we illustrate the diverse biological functionality of the SRCs with regard to their role in immunity. In the light of recent development of SRC small molecule inhibitors and stimulators, we discuss their potential relevance as modulators of the immunological activity of the SRCs for therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: Th17 cells; Treg cells; inflammation; macrophages; nuclear coactivators (NCoAs); nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB); steroid receptor coactivators (SRCs).
Copyright © 2022 Gilad, Lonard and O’Malley.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are paid consultants by and disclose an equity position in CoRegen, Inc.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

