Gene knockdown by structure defined single-stem loop small non-coding RNAs with programmable regulatory activities
- PMID: 36582457
- PMCID: PMC9761848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.11.006
Gene knockdown by structure defined single-stem loop small non-coding RNAs with programmable regulatory activities
Abstract
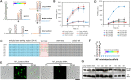
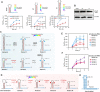
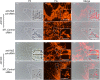
Gene regulation by trans-acting small RNAs (sRNAs) has considerable advantages over other gene regulation strategies. However, synthetic sRNAs mainly take natural sRNAs (MicC or SgrS) as backbones and comprise three functional elements folding into two or more stem-loop structures: an mRNA base pairing region, an Hfq-binding structure, and a rho-independent terminator. Due to limited numbers of natural sRNAs and complicated backbone structures, synthetic sRNAs suffer from low activity programmability and poor structural modularity. Moreover, natural sRNA backbone sequences may increase the possibility of unwanted recombination. Here, we present a bottom-up approach for creating structure defined single-stem loop small non-coding RNAs (ssl-sRNAs), which contain a standardized scaffold of a 7 bp-stem-4 nt-loop-polyU-tail and a 24 nt basing pairing region covering the first eight codons. Particularly, ssl-sRNA requires no independent Hfq-binding structure, as the polyU tail fulfills the roles of binding Hfq. A thermodynamic-based scoring model and a web server sslRNAD (http://www.kangzlab.cn/) were developed for automated design of ssl-sRNAs with well-defined structures and programmable activities. ssl-sRNAs displayed weak polar effects when regulating polycistronic mRNAs. The ssl-sRNA designed by sslRNAD showed regulatory activities in both Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. A streamlined workflow was developed for the construction of customized ssl-sRNA and ssl-sRNA libraries. As examples, the E. coli cell morphology was easily modified and new target genes of ergothioneine biosynthesis were quickly identified with ssl-sRNAs. ssl-sRNA and its designer sslRNAD enable researchers to rapidly design sRNAs for knocking down target genes.
Keywords: De novo design; Ergothioneine; Metabolic engineering; Regulatory RNA; Synthetic biology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Design of artificial small regulatory trans-RNA for gene knockdown in Bacillus subtilis.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022 Nov 14;8(1):61-68. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.11.003. eCollection 2023 Mar. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36474928 Free PMC article.
-
PolyU tail of rho-independent terminator of bacterial small RNAs is essential for Hfq action.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 9;108(32):13059-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107050108. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21788484 Free PMC article.
-
A Modular Genetic System for High-Throughput Profiling and Engineering of Multi-Target Small RNAs.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1737:373-391. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7634-8_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29484604
-
Synthetic small regulatory RNAs in microbial metabolic engineering.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jan;105(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10971-8. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33201273 Review.
-
Regulation of Transcription Termination of Small RNAs and by Small RNAs: Molecular Mechanisms and Biological Functions.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Jun 12;9:201. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00201. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31249814 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Minimizing endogenous cryptic plasmids to construct antibiotic-free expression systems for Escherichia coli Nissle 1917.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 25;9(1):165-175. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.01.006. eCollection 2024 Mar. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38348398 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory RNAs in Bacillus subtilis: A review on regulatory mechanism and applications in synthetic biology.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 10;9(2):223-233. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.01.013. eCollection 2024 Jun. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38385150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory effect of andrographolide on the expression of key regulatory genes in Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation.J Mol Histol. 2024 Dec 23;56(1):53. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10295-1. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 39714542
References
-
- Vanderpool C.K., Gottesman S. Involvement of a novel transcriptional activator and small RNA in post-transcriptional regulation of the glucose phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase system. Mol Microbiol. 2004;54(4):1076–1089. - PubMed
-
- Repoila F., Majdalani N., Gottesman S. Small non-coding RNAs, co-ordinators of adaptation processes in Escherichia coli: the RpoS paradigm. Mol Microbiol. 2003;48(4):855–861. - PubMed
-
- Altuvia S., Weinstein-Fischer D., Zhang A., Postow L., Storz G. A small, stable RNA induced by oxidative stress: role as a pleiotropic regulator and antimutator. Cell. 1997;90(1):43–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

