Evaluation of Triglyceride Glucose Index and Homeostasis Model of Insulin Resistance in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- PMID: 36582617
- PMCID: PMC9793723
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S387942
Evaluation of Triglyceride Glucose Index and Homeostasis Model of Insulin Resistance in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Abstract
Purpose: To use the triglyceride glucose (TyG) index to evaluate insulin resistance (IR) in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and to explore alternative indicators for early identification of IR.
Patients and methods: This study included 114 patients with PCOS and 61 healthy volunteers. Pearson or Spearman correlations were calculated to compare the association between the TyG index and triglyceride glucose body mass index (TyG-BMI) with homeostatic model assessment for IR (HOMA-IR), homeostasis model assessment for β-cell function (HOMA-β), quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI), and fasting glucose-to-insulin ratio (FG-IR). The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of the TyG index and TyG-BMI in identifying IR (defined as HOMA-IR ≥2.5) in patients with PCOS.
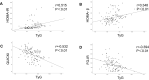
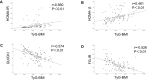
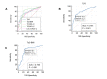
Results: Correlation analyses revealed that the TyG index of the PCOS group was positively correlated with HOMA-IR (r=0.515, P<0.01) and HOMA-β (r=0.348, P<0.01), but negatively correlated with QUICKI (r=-0.532, P<0.01) and FG-IR (r=-0.394, P<0.01). The ROC curve of IR defined by HOMA-IR showed that the AUC value of TyG-BMI was the highest, at 0.796 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.710-0.866, P<0.001) when the cut-off point was 191.53, with 85.3% sensitivity and 73.9% specificity values. For the TyG index, the AUC was 0.781 (95% CI: 0.693-0.853, P<0.001) when 8.51 was the cut-off point, with a sensitivity of 63.2% and specificity of 87.0%.
Conclusion: This study found that the TyG index and TyG-BMI performed better than traditional lipid ratios, such as triglycerides/high density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C), in predicting IR and may be used as markers of IR in Chinese patients with PCOS.
Keywords: fasting glucose-to-insulin ratio; quantitative insulin sensitivity check index; triglyceride glucose body mass index; triglycerides/high density lipoprotein cholesterol.
© 2022 Zheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of lipid ratios and triglyceride-glucose index as risk markers of insulin resistance in Iranian polycystic ovary syndrome women.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Nov 8;19(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01410-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 33161896 Free PMC article.
-
Value of the triglyceride-glucose index and non-traditional blood lipid parameters in predicting metabolic syndrome in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.Hormones (Athens). 2023 Jun;22(2):263-271. doi: 10.1007/s42000-023-00438-6. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Hormones (Athens). 2023. PMID: 36790635
-
Triglycerides/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a predictor similar to the triglyceride-glucose index for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome using International Diabetes Federation criteria of insulin resistance in obese adolescents: a cross-sectional study.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020 May 24;33(6):777-784. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2019-0310. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32447329
-
Challenges in the diagnosis of insulin resistance: Focusing on the role of HOMA-IR and Tryglyceride/glucose index.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022 Aug;16(8):102581. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102581. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022. PMID: 35939943 Review.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index and obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jan 8;23(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02005-3. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38185682 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The triglycerides and glucose index is more strongly associated with metabolically healthy obesity phenotype than the lipid and obesity indices.J Endocrinol Invest. 2024 Apr;47(4):865-871. doi: 10.1007/s40618-023-02201-5. Epub 2023 Sep 28. J Endocrinol Invest. 2024. PMID: 37768526
-
Triglyceride-glucose index and lipid ratios in women with and without polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Mar 31;16:20420188251328840. doi: 10.1177/20420188251328840. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40171216 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-Glucose Index As A Biomarker Of Insulin Resistance, Diabetes Mellitus, Metabolic Syndrome, And Cardiovascular Disease: A Review.EJIFCC. 2024 Apr 11;35(1):44-51. eCollection 2024 Apr. EJIFCC. 2024. PMID: 38706737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between TyG index trajectory and new-onset lean NAFLD: a longitudinal study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 27;15:1321922. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1321922. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38476672 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Influence of Insulin Resistance on Arterial Stiffness in Healthy Adults: From the Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health Insights of the EVasCu Study.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 11;16(6):791. doi: 10.3390/nu16060791. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38542702 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

