Case report: TP53 and RB1 loss may facilitate the transformation from lung adenocarcinoma to small cell lung cancer by expressing neuroendocrine markers
- PMID: 36583000
- PMCID: PMC9792468
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1006480
Case report: TP53 and RB1 loss may facilitate the transformation from lung adenocarcinoma to small cell lung cancer by expressing neuroendocrine markers
Abstract
Introduction: Transformation from lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is one of the mechanisms responsible for acquired EGFR-TKIs resistance. Although it rarely happens this event determines a rapid disease deterioration and needs specific treatment.
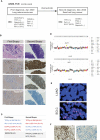
Patient and method: We report a case of 75-year-old LUAD female with a p.L858R mutation in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) who presented with SCLC transformation after responding to first line osimertinib treatment for only 6 months. To understand the underlying molecular mechanism, we retrospectively sequenced the first (LUAD) and the second (SCLC) biopsy using a 56 multi-gene panel. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) was applied to confirm the genetic aberrations identified.
Results: EGFR p.E709A and p.L858R, Tumor Protein p53 (TP53) p.A159D and Retinoblastoma 1 (RB1) c.365-1G>A were detected in both the diagnostic LUAD and transformed SCLC samples. A high copy number gain for Proto-Oncogene C-Myc (MYC) and a Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Alpha (PIK3CA) p.E545K mutation were found in the transformed sample specifically. Strong TP53 staining and negative RB1 staining were observed in both LUAD and SCLC samples, but FISH only identified MYC amplification in SCLC tissue.
Conclusion: We consider the combined presence of MYC amplification with mutations in TP53 and RB1 as drivers of SCLC transformation. Our results highlight the need to systematically evaluate TP53 and RB1 status in LUAD patients to offer a different therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: MYC amplification; TP53 and RB1 loss; lung adenocarcinoma; osimertinib; small cell lung cancer transformation.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Wei, Feng, Wu, Chang, Wang, Yang, Zhang, Han, Zhang, Zheng, Groen, van den Berg, Ma, Li and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EGFR-Mutant Adenocarcinomas That Transform to Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Other Neuroendocrine Carcinomas: Clinical Outcomes.J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 1;37(4):278-285. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01585. Epub 2018 Dec 14. J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30550363 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation or tumor heterogeneity: Mutations in EGFR, SOX2, TP53, and RB1 persist in the histological rapid conversion from lung adenocarcinoma to small-cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Apr;14(11):1036-1041. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14832. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36810856 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent RB1 and TP53 Alterations Define a Subset of EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers at risk for Histologic Transformation and Inferior Clinical Outcomes.J Thorac Oncol. 2019 Oct;14(10):1784-1793. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 19. J Thorac Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31228622 Free PMC article.
-
Histological transformation into SCLC: An important resistance mechanism of NSCLC upon immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 30;14:1275957. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1275957. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small cell lung cancer transformation from EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma: A case report and literatures review.Cancer Biol Ther. 2018 Jun 3;19(6):445-449. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1435222. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29461911 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor grade-associated genomic mutations in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 20;13:1119575. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1119575. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37020866 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Exome Sequencing Study Identifies Distinct Characteristics of Transformed Small Cell Lung Cancer With EGFR Mutation Compared to De Novo Small Cell and Primary Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers.Cancer Med. 2025 Apr;14(7):e70838. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70838. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40197849 Free PMC article.
-
ALK-rearranged and EGFR wild-type lung adenocarcinoma transformed to small cell lung cancer: a case report.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 23;14:1395654. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1395654. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38720809 Free PMC article.
-
Patients outcomes in lung adenocarcinoma transforming to small-cell lung cancer after tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Feb 1;23(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03687-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39893475 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation of lung adenocarcinoma to small cell lung cancer following osimertinib treatment: a case report and literature review.Anticancer Drugs. 2025 Mar 1;36(3):253-259. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001686. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Anticancer Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39792045 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

