Can glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists cause acute kidney injury? An analytical study based on post-marketing approval pharmacovigilance data
- PMID: 36583004
- PMCID: PMC9792852
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1032199
Can glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists cause acute kidney injury? An analytical study based on post-marketing approval pharmacovigilance data
Abstract
Clinical studies after marketing have shown that the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist(GLP-1RA) may lead to acute kidney injury(AKI). However, few epidemiological studies have investigated the risk, clinical features, and outcomes of AKI caused by different GLP-1RA. In this study, Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) data were used to compare the association between different GLP-1RA and AKI in the real world.
Methods: FAERS data from January 2004 to December 2021 were mined using disproportionality analysis and Bayesian analysis to determine the correlation between different GLP-1RA and AKI, and the onset time, mortality, and hospitalization rate of different GLP-1RA were analyzed.
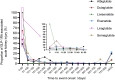
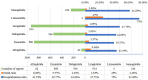
Results: We identified 2670 cases of AKI events associated with GLP-1RA, of which liraglutide was the most commonly reported (34.98%). The patients with AKI were mainly males (47.94%), and the age group was mainly 45-84 years old (73.15%). obese patients with weight more than 99kg (24.42%) were more likely to have AKI. According to different signal mining methods, reporting odds ratio (ROR) (1.50, 95% confidence interval =1.41-1.60) and Bayesian confidence Propagation neural network (0.57, 95% confidence interval =0.54), liraglutide was more strongly associated with AKI than other GLP-1RA. The median time to onset of AKI was 63 days [quartile range (IQR): 15-458.5 days]. In addition, the hospitalization rate and fatality rate of patients with GLP-1RA-related AKI were 45.28% and 4.23% respectively.
Conclusions: Based on the data in the FAERS database, we analyzed the risk, onset time, and adverse reaction outcomes of GLP-1RA-induced AKI in detail. The results showed that liraglutide had the highest risk of AKI. From the early stage of treatment, we need to monitor patients' renal function regularly, especially for patients with high kidney risks such as obesity and age.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; adverse event reporting system; data mining; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; onset time; outcome.
Copyright © 2022 Dong and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postmarket safety profile of suicide/self-injury for GLP-1 receptor agonist: a real-world pharmacovigilance analysis.Eur Psychiatry. 2023 Nov 30;66(1):e99. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2023.2474. Eur Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38031404 Free PMC article.
-
Association between different GLP-1 receptor agonists and gastrointestinal adverse reactions: A real-world disproportionality study based on FDA adverse event reporting system database.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 7;13:1043789. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1043789. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36568085 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoglycemia following the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: a real-world analysis of post-marketing surveillance data.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Sep;9(18):1482. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-4162. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34734034 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in end-staged kidney disease and kidney transplantation: A narrative review.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023 Jun;33(6):1111-1120. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2023.03.023. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2023. PMID: 37100640 Review.
-
GLP-1 Agonist to Treat Obesity and Prevent Cardiovascular Disease: What Have We Achieved so Far?Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2022 Nov;24(11):867-884. doi: 10.1007/s11883-022-01062-2. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2022. PMID: 36044100 Review.
Cited by
-
An Observational Study of Cardiovascular Outcomes of Tirzepatide vs Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists.JACC Adv. 2025 May;4(5):101740. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2025.101740. JACC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40447342 Free PMC article.
-
Semaglutide-associated kidney injury.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Aug 13;17(9):sfae250. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae250. eCollection 2024 Sep. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 39258261 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists on weight and cardiovascular outcomes: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 1;103(44):e40364. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040364. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39496023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suicidal thoughts and behaviors associated with fluoroquinolone antibiotics: a real-world pharmacovigilance analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 25;16:1556159. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1556159. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40351425 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional priorities to support GLP-1 therapy for obesity: A joint advisory from the American College of Lifestyle Medicine, the American Society for Nutrition, the Obesity Medicine Association, and the Obesity Society.Obes Pillars. 2025 Jun 3;15:100181. doi: 10.1016/j.obpill.2025.100181. eCollection 2025 Sep. Obes Pillars. 2025. PMID: 40673264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

