Vitamin D pathway gene variation rs3740165 is associated with serological uric acid levels in healthy Chinese women
- PMID: 36583005
- PMCID: PMC9792855
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1059964
Vitamin D pathway gene variation rs3740165 is associated with serological uric acid levels in healthy Chinese women
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the relationship between gene polymorphisms involved in the vitamin D metabolic pathway and serum uric acid (UA) levels in Chinese women.
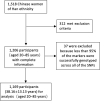
Methods: Fifteen key genes within the vitamin D metabolic pathway were screened using 96 single nucleotide polymorphisms in a group of 1,206 (37.96 ± 13.08 years) unrelated healthy Chinese women (aged 20-85 years). Blood and urine tests were performed at the same time. The Wilcoxon Mann-Whitney test was used to compare groups aged ≤50 years and >50 years. The mean serum UA values were computed within each group of homozygous referent, heterozygous, and homozygous variant genotypes for each single nucleotide polymorphism.
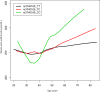
Results: The exclusion process left 1,169 participants (38.16 ± 13.13 years) for analysis. One single nucleotide polymorphism in the CUBN gene (rs3740165) was identified as being significantly associated with serum UA levels in the group aged over 50 years. The wild type (C/C) population had higher serum UA levels in this group (P<0.001). In women aged over 50 years, allele C was associated with a higher risk of hyperuricemia than allele T (odds ratio 2.752, 95% confidence interval 1.458-5.192; P = 0.002). There was also a higher risk of hyperuricemia in genotype TC + CC compared with genotype TT (odds ratio 3.326, 95% confidence interval 1.513-7.313; P = 0.003) in women over 50 years of age.
Conclusion: The results suggest that the CUBN gene contributes to variability in serum UA levels in healthy Chinese Han women over 50 years of age.
Keywords: gene; pathway; polymorphism; uric acid; vitamin D.
Copyright © 2022 Gu, Yue, Wang, Zhang, Hu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Allele C of rs6068816 in the CYP24A1 Gene is Associated with Increased Risk of Hyperuricemia in the Chinese Population: A Case-Control Study.Discov Med. 2024 Nov;36(190):2224-2230. doi: 10.24976/Discov.Med.202436190.204. Discov Med. 2024. PMID: 39600277
-
Association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (C677T) polymorphism with hyperuricemia.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2007 Jul;17(6):462-7. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2006.02.002. Epub 2006 Sep 28. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2007. PMID: 17010581
-
Association of ABCG2 rs2231142-A allele and serum uric acid levels in male and obese individuals in a Han Taiwanese population.J Formos Med Assoc. 2017 Jan;116(1):18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2015.12.002. Epub 2016 Jan 17. J Formos Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 26792383
-
Serum uric acid concentrations and risk of intracerebral hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Atherosclerosis. 2018 Aug;275:352-358. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Atherosclerosis. 2018. PMID: 30015299
-
Association Between Vitamin D and Uric Acid in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Horm Metab Res. 2020 Oct;52(10):732-741. doi: 10.1055/a-1240-5850. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Horm Metab Res. 2020. PMID: 33049785 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources