A hypoxia risk score for prognosis prediction and tumor microenvironment in adrenocortical carcinoma
- PMID: 36583015
- PMCID: PMC9792869
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.796681
A hypoxia risk score for prognosis prediction and tumor microenvironment in adrenocortical carcinoma
Abstract
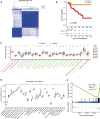
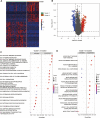
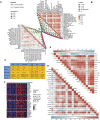
Background: Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is a rare malignant endocrine tumor derived from the adrenal cortex. Because of its highly aggressive nature, the prognosis of patients with adrenocortical carcinoma is not impressive. Hypoxia exists in the vast majority of solid tumors and contributes to invasion, metastasis, and drug resistance. This study aimed to reveal the role of hypoxia in Adrenocortical carcinoma and develop a hypoxia risk score (HRS) for Adrenocortical carcinoma prognostic prediction. Methods: Hypoxia-related genes were obtained from the Molecular Signatures Database. The training cohorts of patients with adrenocortical carcinoma were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas, while another three validation cohorts with comprehensive survival data were collected from the Gene Expression Omnibus. In addition, we constructed a hypoxia classifier using a random survival forest model. Moreover, we explored the relationship between the hypoxia risk score and immunophenotype in adrenocortical carcinoma to evaluate the efficacy of immune check inhibitors (ICI) therapy and prognosis of patients. Results: HRS and tumor stage were identified as independent prognostic factors. HRS was negatively correlated with immune cycle activity, immune cell infiltration, and the T cell inflammatory score. Therefore, we considered the low hypoxia risk score group as the inflammatory immunophenotype, whereas the high HRS group was a non-inflammatory immunophenotype. In addition, the HRS was negatively related to the expression of common immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-L1, CD200, CTLA-4, and TIGIT, suggesting that patients with a lower hypoxia risk score respond better to immunotherapy. Conclusion: We developed and validated a novel hypoxia risk score to predict the immunophenotype and response of patients with adrenocortical carcinoma to immune check inhibitors therapy. These findings not only provide fresh prognostic indicators for adrenocortical carcinoma but also offer several promising treatment targets for this disease.
Keywords: Adrenocortical carcinoma; hypoxia; immunotherapy; risk score; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Deng, Li, Fu, Pu, Zhang, Chen, Tong and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer WP declared a shared parent affiliation with the authors to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of Hypoxia-Related Subtypes, Establishment of Prognostic Models, and Characteristics of Tumor Microenvironment Infiltration in Colon Cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 17;13:919389. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.919389. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35783281 Free PMC article.
-
A Robust Hypoxia Risk Score Predicts the Clinical Outcomes and Tumor Microenvironment Immune Characters in Bladder Cancer.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 13;12:725223. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.725223. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484235 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic Characteristic Genes Predict Response to Immunotherapy for Urothelial Carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 25;9:762478. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.762478. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34901008 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of m6A-Related Signatures in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Identification of Clinical Prognostic Regulators in Adrenocortical Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 3;12:637933. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637933. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33746977 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Microenvironment in Adrenocortical Carcinoma: Barrier to Immunotherapy Success?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 9;13(8):1798. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081798. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33918733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

