Crocin: Functional characteristics, extraction, food applications and efficacy against brain related disorders
- PMID: 36583211
- PMCID: PMC9792498
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1009807
Crocin: Functional characteristics, extraction, food applications and efficacy against brain related disorders
Abstract
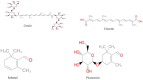
Crocin is a bioactive compound that naturally occurs in some medicinal plants, especially saffron and gardenia fruit. Different conventional and novel methods are used for its extraction. Due to some control conditions, recent methods such as ultrasonic extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, enzyme-associated extraction, microwave extraction, and pulsed electric field extraction are widely used because these methods give more yield and efficiency. Crocin is incorporated into different food products to make functional foods. However, it can also aid in the stability of food products. Due to its ability to protect against brain diseases, the demand for crocin has been rising in the pharmaceutical industry. It also contain antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer and antidepressant qualities. This review aims to describe crocin and its role in developing functional food, extraction, and bioavailability in various brain-related diseases. The results of the literature strongly support the importance of crocin against various diseases and its use in making different functional foods.
Keywords: brain disorders; crocin; extraction techniques; food applications; medicinal.
Copyright © 2022 Ali, Yu, Kousar, Khalid, Maqbool, Aziz, Arshad, Aadil, Trif, Riaz, Shaukat, Manzoor and Qin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential Role of Phytochemical Extract from Saffron in Development of Functional Foods and Protection of Brain-Related Disorders.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Sep 22;2022:6480590. doi: 10.1155/2022/6480590. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36193081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of gardenia fruit oil with bioactive components and their identification and quantification by HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS(2).Food Funct. 2015 Jul;6(7):2194-204. doi: 10.1039/c5fo00205b. Food Funct. 2015. PMID: 26040554
-
Understanding the potential benefits of thyme and its derived products for food industry and consumer health: From extraction of value-added compounds to the evaluation of bioaccessibility, bioavailability, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(18):2879-2895. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1477730. Epub 2018 Jun 14. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 29771598 Review.
-
Bioactivity assessment and toxicity of crocin: a comprehensive review.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Feb;64:65-80. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.016. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24275090 Review.
-
Saffron bioactives crocin, crocetin and safranal: effect on oxidative stress and mechanisms of action.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(12):3232-3249. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1864279. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33356506 Review.
Cited by
-
Carotenoid Supplementation for Alleviating the Symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 18;25(16):8982. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168982. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional, biochemical, and clinical applications of carob: A review.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Jun 9;11(7):3641-3654. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3367. eCollection 2023 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37457186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Update on Carotenoid Colorants from Plants and Microalgae: Challenges and Advances from Research Laboratories to Industry.Foods. 2023 Nov 10;12(22):4080. doi: 10.3390/foods12224080. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38002140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization of spray dried yogurt and its application to prepare functional cookies.Front Nutr. 2023 May 9;10:1186469. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1186469. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37229469 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-component screening coupled with ultrasound-assisted green extraction based on HPLC-HRMS for bio-actives analysis in saffron (Crocus sativus L.).Food Chem X. 2025 Jan 26;25:102236. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102236. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 39974536 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dhiman N, Kharkwal H. Biosynthesis and Derivatization of the Major Phytoconstituents of Saffron. Saffron: Elsevier; (2020). p. 83–92.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

