KLF13 overexpression protects sepsis-induced myocardial injury and LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis
- PMID: 36583453
- PMCID: PMC9845607
- DOI: 10.1111/iep.12459
KLF13 overexpression protects sepsis-induced myocardial injury and LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis
Abstract
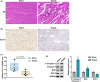
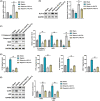
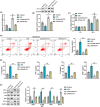
Sepsis remains a worldwide public health problem. This study aims to explore the role and mechanism of transcriptional factors (TFs) in sepsis-induced myocardial injury. Firstly, TF KLF13 was selected to explore its role in sepsis-induced myocardial injury. The caecal ligation and puncture (CLP) -induced sepsis mouse model was established and the septic mice were examined using standard histopathological methods. KLF13 expression was detected in the septic mouse heart and was also seen in a lipoploysaccharide (LPS) -induced cellular inflammation model. To explore this further both pro-apoptotic cleaved-caspase3/caspase3 and Bax levels and anti-apoptotic Bcl2 levels were examined, also in both models, In addition inflammatory cytokine (IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-8 and MCP-1) production and IκB-α protein level and p65 phosphorylation were examined in both septic mice and LPS-induced cells. Thus three parameters - cardiomyocyte apoptosis, inflammatory response and NF-κB pathway activation were evaluated under similar conditions. The septic mice showed significant oedema, disordered myofilament arrangement and degradation and necrosis to varying degrees in the myocardial cells. KLF13 was downregulated in both the septic mouse heart and the LPS-induced cellular inflammation model. Furthermore, both models showed abnormally increased cardiomyocyte apoptosis (increased cleaved-caspase3/caspase and Bax protein levels and decreased Bcl2 level), elevated inflammation (increased production of inflammatory cytokines) and the activated NF-κB pathway (increased p65 phosphorylation and decreased IκB-α protein level). KLF13 overexpression notably ameliorated sepsis-induced myocardial injury in vivo and in vitro. KLF13 overexpression protected against sepsis-induced myocardial injury and LPS-induced cellular inflammation and apoptosis via inhibiting the inflammatory pathways (especially NF-κB signalling) and cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Keywords: KLF13; cardiomyocyte apoptosis; inflammation; myocardial injury; sepsis; transcriptional factors.
© 2022 Company of the International Journal of Experimental Pathology (CIJEP).
Conflict of interest statement
N/A
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpressing six-transmembrane protein of prostate 2 (STAMP2) alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury probably by hindering M1 macrophage polarization via the NF-κB pathway.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2023;61(1):34-46. doi: 10.5603/FHC.a2022.0032. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2023. PMID: 36583372
-
Pretreatment with interleukin-15 attenuates inflammation and apoptosis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction.Eur J Histochem. 2024 Apr 29;68(2):4019. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2024.4019. Eur J Histochem. 2024. PMID: 38686889 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA NEAT1 alleviates sepsis-induced myocardial injury by regulating the TLR2/NF-κB signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jun;23(11):4898-4907. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201906_18078. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31210324
-
[Mechanisms of sodium butyrate inhibition of microglia inflammatory activation in hippocampus via Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB p65 pathway].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Dec;33(12):1471-1478. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20211105-01647. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 35131015 Chinese.
-
Flavonoid fisetin alleviates kidney inflammation and apoptosis via inhibiting Src-mediated NF-κB p65 and MAPK signaling pathways in septic AKI mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Feb;122:109772. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109772. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31918290
Cited by
-
Putting transcriptional brakes on fibrosis: a negative regulator of TGFβ signaling.Trends Cell Biol. 2023 Sep;33(9):734-735. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.06.003. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Trends Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37380582 Free PMC article.
-
miR-361-3p overexpression promotes apoptosis and inflammation by regulating the USP49/IκBα/NF-κB pathway to aggravate sepsis-induced myocardial injury.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Nov 19;13(6):tfae190. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae190. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39568464
-
Cecropin A Alleviates LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis of Bovine Endometrial Epithelial Cells.Animals (Basel). 2024 Feb 29;14(5):768. doi: 10.3390/ani14050768. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473153 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and treatment strategies of sepsis-induced myocardial injury: modern and traditional medical perspectives.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 May 15;21(8):3478-3504. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.111288. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40520010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatic Evaluation of KLF13 Genetic Variant: Implications for Neurodevelopmental and Psychiatric Symptoms.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 11;15(8):1056. doi: 10.3390/genes15081056. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carey MG, Valcin EK, Lent D, White M. Nursing Care for the Initial Resuscitation of severe sepsis patients. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2021;33(3):263‐274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

