The off-label uses of pipeline embolization device for complex cerebral aneurysms: Mid-term follow-up in a single center
- PMID: 36583531
- PMCID: PMC12035148
- DOI: 10.1177/15910199221148800
The off-label uses of pipeline embolization device for complex cerebral aneurysms: Mid-term follow-up in a single center
Abstract
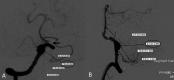
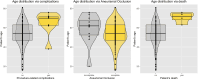
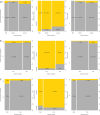
ObjectiveTo describe the off-label uses of pipeline embolization device for a variety of types of aneurysms including ruptured aneurysms, posterior circulation aneurysms, small aneurysms, distal aneurysms, and recurrent aneurysms.MethodsClinical and angiographic data of patients who underwent pipeline embolization device treatment on off-label use at our center were retrospectively reviewed. For categorical variables, Fisher's exact test was used, and a two-sample Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used for patients' age to analyze the correlation with outcomes.ResultsIn this study, 121 aneurysms in 107 patients received off-label pipeline embolization device treatments. The overall rate of complete aneurysm occlusion was 77.8% (28/36 in 35 patients) for posterior circulation aneurysms and 95.3% (81/85 in 72 patients) for anterior circulation aneurysms. The posterior circulation aneurysms have a lower rate of aneurysm occlusion (p = 0.0372). The small aneurysms have a higher rate of aneurysm occlusion (p = 0.0104). The patient's sex, age, and aneurismal size were associated with ischemic stroke complications (p = 0.0397, 0.0166, and 0.0178). In posterior circulation aneurysm patients, only two basilar apex aneurysms underwent pipeline embolization device treatment, both of whom died of thrombotic complications. There was no difference in mortality between posterior circulation aneurysm patients (8.6%, 3/35) and anterior circulation aneurysm patients (1.4%, 1/72) (p = 0.1015). Patients of older age have a higher risk of death rate (p = 0.0053).ConclusionsThe off-label use of pipeline embolization device is often performed in clinical practice and can achieve efficacy in complex aneurysms. The off-label use of pipeline embolization device was found to carry an increased rate of mortality in older patients. Excluding basilar apex aneurysms, the pipeline embolization device is as safe as anterior circulation aneurysms in the treatment of posterior circulation aneurysms elsewhere.
Keywords: Pipeline embolization device; cerebral aneurysm; endovascular; off-label.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Cler SJ, Lauzier DC, Chatterjee ARet al. et al. Comparative study of on-label versus off-label treatment of intracranial aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device. J Neurosurg 2022 Jan 28; 1–6. - PubMed
-
- Patel PD, Chalouhi N, Atallah Eet al. Off-label uses of the pipeline embolization device: a review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 2017; 42: E4. - PubMed
-
- Vakharia K, Munich SA, Waqas Met al. et al. Treatment of anterior circulation aneurysms in the internal carotid artery with flow diverters. Neurosurgery 2020; 86: S55–S63. - PubMed
-
- Lv X, Chen Z, Liu Let al. et al. Rupture of intradural giant aneurysms: the mode of treatment, anatomical, and mechanical factors. Neurol India 2019; 67: 1194–1199. - PubMed
-
- Lv X, Ge H, He Het al. et al. A systematic review of pipeline embolization device for giant intracranial aneurysms. Neurol India 2017; 65: 35–38. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

