Clinical value of AKR1B10 in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36584078
- PMCID: PMC9803170
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279591
Clinical value of AKR1B10 in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the clinical value of Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 (AKR1B10) in the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
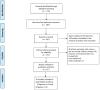
Methods: A search of the PubMed, China Biology Medicine, Cochrane, and Embase databases was performed to conduct meta-analyses to evaluate the accuracy of AKR1B10 in diagnosing HCC and to assess the impact on prognosis of patients after curative resection of HCC.
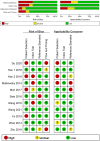
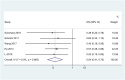
Results: A total of 12 different cohorts from 11 studies including 2747 HCC patients and 2053 controls showed that the pooled specificity and the pooled sensitivity of AKR1B10 for the diagnosis of HCC were 0.78 (95% CI: 0.69-0.85) and 0.85 (95% CI: 0.77-0.90), respectively. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of serum AKR1B10 for the diagnosis of HCC were 0.80 (95% CI: 0.70-0.86) and 0.87 (95% CI: 0.77-0.93), respectively. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of AKR1B10 in malignant tumor tissue for the diagnosis of HCC were 0.78 (95% CI: 0.61-0.89) and 0.82 (95% CI: 0.69-0.90), respectively. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of AKR1B10 to distinguish HCC from benign liver disease were 0.71 (95% CI: 0.62-0.78) and 0.84 (95% CI: 0.77-0.89), respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of AKR1B10 combined with alpha fetoprotein (AFP) in the diagnosis of HCC were 0.84 (95% CI: 0.79-0.88) and 0.88 (95% CI: 0.73-0.95), respectively. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of AKR1B10 in malignant tumor tissue for the diagnosis of early-stage HCC were 0.85 (95% CI: 0.62-0.95) and 0.88 (95% CI: 0.81-0.93), respectively. A meta-analysis of five studies including 798 patients demonstrated that high AKR1B10 expression in liver malignant tumor was associated with better overall survival in patients with HCC after hepatectomy (HR = 0.54, 95% CI: 0.41-0.72, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: AKR1B10 exhibits a great clinical value in the diagnosis of HCC, especially for early-stage HCC, with excellent diagnostic accuracy. Furthermore, AKR1B10 expression can predict the prognosis of HCC patients after hepatic resection.
Copyright: © 2022 Wang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Large-Scale Multicenter Study Validates Aldo-Keto Reductase Family 1 Member B10 as a Prevalent Serum Marker for Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Hepatology. 2019 Jun;69(6):2489-2501. doi: 10.1002/hep.30519. Epub 2019 Apr 6. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30672601 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulated aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 in chronic hepatitis C: association with serum alpha-fetoprotein and hepatocellular carcinoma.Liver Int. 2012 Oct;32(9):1382-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2012.02827.x. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Liver Int. 2012. PMID: 22681639 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemistry Detects Increased Expression of Aldo-Keto Reductase Family 1 Member B10 (AKR1B10) in Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Oct 17;24:7414-7423. doi: 10.12659/MSM.910738. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30328412 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of AKR1B10 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Apr 5;11(4):486. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040486. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30959792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II versus alpha-fetoprotein in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review with meta-analysis.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018 Dec;17(6):487-495. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2018.09.009. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018. PMID: 30257796
Cited by
-
AKR1B10 and digestive tumors development: a review.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 16;15:1462174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1462174. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39737179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aldo-keto reductases: Role in cancer development and theranostics.Oncol Res. 2024 Jul 17;32(8):1287-1308. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.049918. eCollection 2024. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39055885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AKR1B10 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway.Oncol Lett. 2023 Nov 15;27(1):18. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.14151. eCollection 2024 Jan. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 38034486 Free PMC article.
-
AKR1B10 as a novel prognostic biomarker linking methylation and immune escape in hepatocellular carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 14;16(1):1551. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03017-w. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40813509 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Aldo-Keto Reductase Family 1 Member B10 (AKR1B10) as a Potential Biomarker for Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jan 16;11:131-143. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S443006. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 38250307 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

