Effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 36584211
- PMCID: PMC9803203
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279889
Effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objective: Type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM) is closely related to sarcopenic obesity(SO). Body composition measurement including body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, percentage body fat, fat mass, muscle mass, visceral adipose tissue and subcutaneus adipose tissue, plays a key role in evaluating T2DM and SO. The weight reduction effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2(SGLT-2) inhibitors has been demonstrated. However, there are warnings that SGLT-2 inhibitors should be used with caution because they may increase the risk of sarcopenia. The effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on body composition in T2DM is inconclusive. In this work, a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials was conducted to evaluate the effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on body composition in T2DM.
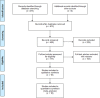
Methods: PubMed, the Cochrane Library, EMbase and Web of Science databases were searched by computer. All statistical analyses were carried out with Review Manager version 5. 3. Results were compared by weight mean difference(WMD), with 95% confidence intervals(CI) for continuous outcomes. A random effects model was applied regardless of heterogeneity. The I2 statistic was applied to evaluate the heterogeneity of studies. Publication bias was assessed using Funnel plots.
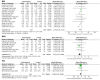
Results: 18 studies with 1430 participants were eligible for the meta-analysis. SGLT-2 inhibitors significantly reduced body weight(WMD:-2. 73kg, 95%CI: -3. 32 to -2. 13, p<0. 00001), body mass index(WMD:-1. 13kg/m2, 95%CI: -1. 77 to -0. 50, p = 0. 0005), waist circumference(WMD:-2. 20cm, 95%CI: -3. 81 to -0. 58, p = 0. 008), visceral fat area(MD:-14. 79cm2, 95%CI: -24. 65 to -4. 93, p = 0. 003), subcutaneous fat area(WMD:-23. 27cm2, 95% CI:-46. 44 to -0. 11, P = 0. 05), fat mass(WMD:-1. 16kg, 95%CI: -2. 01 to -0. 31, p = 0. 008), percentage body fat(WMD:-1. 50%, 95%CI:-2. 12 to -0. 87, P<0. 00001), lean mass(WMD:-0. 76kg, 95%CI:-1. 53 to 0. 01, P = 0. 05) and skeletal muscle mass(WMD:-1. 01kg, 95%CI:-1. 91 to -0. 11, P = 0. 03).
Conclusion: SGLT-2 inhibitors improve body composition in T2DM including body weight, body mass index, waist circumference, visceral fat area, subcutaneous fat area, percentage body fat and fat mass reduction, but cause adverse effects of reducing muscle mass. Therefore, until more evidence is obtained to support that SGLT-2 inhibitors increase the risk of sarcopenia, not only the benefit on body composition, but also the adverse effect of the reduction in muscle mass by SGLT-2 inhibitors in T2DM should be considered.
Copyright: © 2022 Pan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors on sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 3;14:1203666. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1203666. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37465122 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors on adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023 May 31;15(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13098-023-01085-y. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023. PMID: 37254186 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 17;12:635556. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.635556. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34220701 Free PMC article.
-
The different hypoglycemic effects between East Asian and non-Asian type 2 diabetes patients when treated with SGLT-2 inhibitors as an add-on treatment for metformin: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 11;13(9):12748-12765. doi: 10.18632/aging.202945. Epub 2021 May 11. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33973870 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on adipose tissue in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 27;14:1115321. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1115321. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36777342 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Renoprotective Mechanisms of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT2i)-A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 27;25(13):7057. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137057. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time Trends of Body Mass Index and its Impact on Glycemic Control Among Finnish Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.Diabetes Ther. 2025 Aug;16(8):1665-1679. doi: 10.1007/s13300-025-01763-2. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Diabetes Ther. 2025. PMID: 40524131 Free PMC article.
-
Age Is Just a Number: Progress and Obstacles in the Discovery of New Candidate Drugs for Sarcopenia.Cells. 2023 Nov 11;12(22):2608. doi: 10.3390/cells12222608. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37998343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of SGLT2 inhibitors beyond glycaemic control.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024 Aug;20(8):513-529. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00836-y. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38671190 Review.
-
Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Body Composition and Fluid Status in Cardiovascular Rehabilitation Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Dec 21;60(12):2096. doi: 10.3390/medicina60122096. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39768974 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

