Effect of ultrasonic power on the stability of low-molecular-weight oyster peptides functional-nutrition W1/O/W2 double emulsion
- PMID: 36584561
- PMCID: PMC9830313
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106282
Effect of ultrasonic power on the stability of low-molecular-weight oyster peptides functional-nutrition W1/O/W2 double emulsion
Abstract
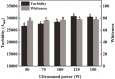
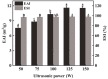
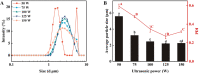
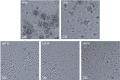
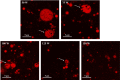
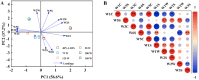
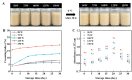
Ultrasonic-assisted treatment is an eco-friendly and cost-effective emulsification method, and the acoustic cavitation effect produced by ultrasonic equipment is conducive to the formation of stable emulsion. However, its effect on the underlying stability of low-molecular-weight oyster peptides (LOPs) functional-nutrition W1/O/W2 double emulsion has not been reported. The effects of different ultrasonic power (50, 75, 100, 125, and 150 W) on the stability of double emulsions and the ability to mask the fishy odor of LOPs were investigated. Low ultrasonic power (50 W and 75 W) treatment failed to form a well-stabilized double emulsion, and excessive ultrasound treatment (150 W) destroyed its structure. At an ultrasonic power of 125 W, smaller particle-sized double emulsion was formed with more uniform distribution, more whiteness, and a lower viscosity coefficient. Meanwhile, the cavitation effect generated by 125 W ultrasonic power improved storage, and oxidative stabilities, emulsifying properties of double emulsion by reducing the droplet size and improved sensorial acceptability by masking the undesirable flavor of LOPs. The structure of the double emulsion was further confirmed by optical microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy. The ultrasonic-assisted treatment is of potential value for the industrial application of double emulsion in functional-nutrition foods.
Keywords: Double emulsion; Electronic nose; Low-molecular-weight oyster peptides; Stability; Ultrasonic power.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fabrication of emulsions prepared by rice bran protein hydrolysate and ferulic acid covalent conjugate: Focus on ultrasonic emulsification.Ultrason Sonochem. 2022 Aug;88:106064. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106064. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Ultrason Sonochem. 2022. PMID: 35749957 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and drying of water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) double emulsion to encapsulate soy peptides.Food Res Int. 2021 Mar;141:110148. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110148. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Food Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33642014
-
Incorporation of water-in-oil-in-water (W1/O/W2) double emulsion in a set-type yogurt model.Food Res Int. 2017 Oct;100(Pt 2):122-131. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.08.027. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Food Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28888432
-
Ultrasonic and homogenization: An overview of the preparation of an edible protein-polysaccharide complex emulsion.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2023 Nov;22(6):4242-4281. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.13221. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2023. PMID: 37732485 Review.
-
Crystallization of lipids and lipid emulsions treated by power ultrasound: A review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(7):1882-1893. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2119365. Epub 2022 Sep 8. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36073738 Review.
Cited by
-
Influences of ultrasonic treatment on the physicochemical properties and microstructure of diacylglycerol-loaded emulsion stabilized with soybean protein isolate and sodium alginate.Ultrason Sonochem. 2024 Aug;108:106981. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.106981. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Ultrason Sonochem. 2024. PMID: 38981339 Free PMC article.
-
An Updated Comprehensive Overview of Different Food Applications of W1/O/W2 and O1/W/O2 Double Emulsions.Foods. 2024 Feb 2;13(3):485. doi: 10.3390/foods13030485. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38338620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intelligent Evaluation and Dynamic Prediction of Oysters Freshness with Electronic Nose Non-Destructive Monitoring and Machine Learning.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Oct 14;14(10):502. doi: 10.3390/bios14100502. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451715 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of physicochemical properties and quercetin delivery ability of fermentation-induced soy protein isolate emulsion gel processed by ultrasound.Ultrason Sonochem. 2024 Jul;107:106902. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.106902. Epub 2024 May 8. Ultrason Sonochem. 2024. PMID: 38797128 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin-loaded oil body emulsions prepared by an ultrasonic and pH-driven method: Fundamental properties, stability, and digestion characteristics.Ultrason Sonochem. 2023 Dec;101:106711. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106711. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023. PMID: 38061250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Y., Selomulya C. Spray drying strategy for encapsulation of bioactive peptide powders for food applications. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020;31:409–415. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2019.10.034. - DOI
-
- Hao L., Wang X., Cao Y., Xu J., Xue C. A comprehensive review of oyster peptides: Preparation, characterisation and bioactivities. Rev. Aquac. 2022;14:120–138. doi: 10.1111/raq.12588. - DOI
-
- Xiang X.W., Zheng H.Z., Wang R., Chen H., Xiao J.X., Zheng B., Liu S.L., Ding Y.T. Ameliorative Effects of Peptides Derived from Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) on Immunomodulatory Function and Gut Microbiota Structure in Cyclophosphamide-Treated Mice. Mar. Drugs. 2021;19:456. doi: 10.3390/md19080456. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li J., Yang L., Li G., Liu S., Cao W., Lin H., Chen Z., Qin X., Huang J., Zheng H. Low-molecular-weight oyster peptides ameliorate cyclophosphamide-chemotherapy side-effects in Lewis lung cancer mice by mitigating gut microbiota dysbiosis and immunosuppression. J. Funct. Foods. 2022;95 doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2022.105196. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

