Acylations in cardiovascular biology and diseases, what's beyond acetylation
- PMID: 36584593
- PMCID: PMC9808004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104418
Acylations in cardiovascular biology and diseases, what's beyond acetylation
Abstract
Metabolism regulates cardiovascular biology through multiple mechanisms, including epigenetic modifications. Over the past two decades, experimental and preclinical studies have highlighted the critical roles of histone modifications in cardiovascular development, homeostasis, and diseases. The widely studied histone acetylation is critical in cardiovascular biology and diseases, and inhibitors of histone deacetylases show therapeutic values. In addition to lysine acetylation, a series of novel non-acetyl lysine acylations have recently been recognized. These non-acetyl lysine acylations have been demonstrated to have physiological and pathological functions, and recent studies have analyzed the roles of these non-acetyl lysine acylations in cardiovascular biology. Herein, we review the current advances in the understanding of non-acetyl lysine acylations in cardiovascular biology and discuss open questions and translational perspectives. These new pieces of evidence provide a more extensive insight into the epigenetic mechanisms underlying cardiovascular biology and help assess the feasibility of targeting acylations to treat cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Cardiovascular biology; Cardiovascular disease; Epigenetics; Metabolism; Metabolite; Non-acetyl acylation.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
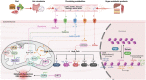
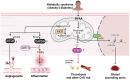
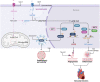

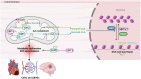
References
-
- Virani S.S., Alonso A., Aparicio H.J., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation. 2021;143(8):e254–e743. - PubMed
-
- Chen X.-F., Chen X., Tang X. Short-chain fatty acid, acylation and cardiovascular diseases. Clinical Science. 2020;134(6):657–676. - PubMed
-
- Li P., Ge J., Li H. Lysine acetyltransferases and lysine deacetylases as targets for cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(2):96–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

