Microbiota-induced lipid peroxidation impairs obeticholic acid-mediated antifibrotic effect towards nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice
- PMID: 36584600
- PMCID: PMC9830314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102582
Microbiota-induced lipid peroxidation impairs obeticholic acid-mediated antifibrotic effect towards nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice
Abstract
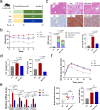
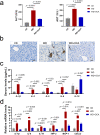
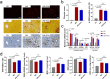
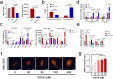
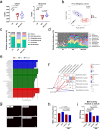
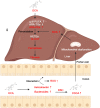
Obeticholic acid (OCA) has been examined to treat non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), but has unsatisfactory antifibrotic effect and deficient responsive rate in recent phase III clinical trial. Using a prolonged western diet-feeding murine NASH model, we show that OCA-shaped gut microbiota induces lipid peroxidation and impairs its anti-fibrotic effect. Mechanically, Bacteroides enriched by OCA deconjugates tauro-conjugated bile acids to generate excessive chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), resulting in liver ROS accumulation. We further elucidate that OCA reduces triglycerides containing polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA-TGs) levels, whereas elevates free PUFAs and phosphatidylethanolamines containing PUFA (PUFA-PEs), which are susceptible to be oxidized to lipid peroxides (notably arachidonic acid (ARA)-derived 12-HHTrE), inducing hepatocyte ferroptosis and activating hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Inhibiting lipid peroxidation with pentoxifylline (PTX) rescues anti-fibrotic effect of OCA, suggesting combination of OCA and lipid peroxidation inhibitor could be a potential antifibrotic pharmacological approach in clinical NASH-fibrosis.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Sinal C.J., Tohkin M., Miyata M., Ward J.M., Lambert G., Gonzalez F.J. Targeted disruption of the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell. 2000;102:731–744. - PubMed
-
- Huang W., Ma K., Zhang J., Qatanani M., Cuvillier J., Liu J., Dong B., Huang X., Moore D.D. Nuclear receptor-dependent bile acid signaling is required for normal liver regeneration. Science. 2006;312:233–236. - PubMed
-
- Sun L., Cai J., Gonzalez F.J. The role of farnesoid X receptor in metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal and liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021;18:335–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

