TRPM1 promotes tumor progression in acral melanoma by activating the Ca2+/CaMKIIδ/AKT pathway
- PMID: 36585114
- PMCID: PMC9811324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.03.005
TRPM1 promotes tumor progression in acral melanoma by activating the Ca2+/CaMKIIδ/AKT pathway
Abstract
Introduction: Acral melanoma is a predominant and aggressive subtype of melanoma in non-Caucasian populations. There is a lack of genotype-driven therapies for over 50% of patients. TRPM1 (transient receptor potential melastatin 1), a nonspecific cation channel, is mainly expressed in retinal bipolar neurons and skin. Nonetheless, the function of TRPM1 in melanoma progression is poorly understood.
Objectives: We investigated the association between TRPM1 and acral melanoma progression and revealed the molecular mechanisms by which TRPM1 promotes tumor progression and malignancy.
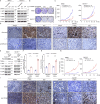
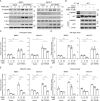
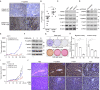
Methods: TRPM1 expression and CaMKII phosphorylation in tumor specimens were tested by immunohistochemistry analysis and scored by two independent investigators. The functions of TRPM1 and CaMKII were assessed using loss-of-function and gain-of-function approaches and examined by western blotting, colony formation, cell migration and invasion, and xenograft tumor growth assays. The effects of a CaMKII inhibitor, KN93, were evaluated using both in vitro cell and in vivo xenograft mouse models.
Results: We revealed that TRPM1 protein expression was positively associated with tumor progression and shorter survival in patients with acral melanoma. TRPM1 promoted AKT activation and the colony formation, cell mobility, and xenograft tumor growth of melanoma cells. TRPM1 elevated cytosolic Ca2+ levels and activated CaMKIIδ (Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIδ) to promote the CaMKIIδ/AKT interaction and AKT activation. The functions of TRPM1 in melanoma cells were suppressed by a CaMKII inhibitor, KN93. Significant upregulation of phospho-CaMKII levels in acral melanomas was related to increased expression of TRPM1. An acral melanoma cell line with high expression of TRPM1, CA11, was isolated from a patient to show the anti-tumor activity of KN93 in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: TRPM1 promotes tumor progression and malignancy in acral melanoma by activating the Ca2+/CaMKIIδ/AKT pathway. CaMKII inhibition may be a potential therapeutic strategy for treating acral melanomas with high expression of TRPM1.
Keywords: Acral melanoma; Ca(2+) channel; CaMKII; TRPM1.
Copyright © 2022. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TRPM1 forms ion channels associated with melanin content in melanocytes.Sci Signal. 2009 May 12;2(70):ra21. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000146. Sci Signal. 2009. PMID: 19436059 Free PMC article.
-
NETO2 promotes melanoma progression via activation of the Ca2+/CaMKII signaling pathway.Front Med. 2023 Apr;17(2):263-274. doi: 10.1007/s11684-022-0935-0. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 36738427
-
BAFF inhibits autophagy promoting cell proliferation and survival by activating Ca2+-CaMKII-dependent Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in normal and neoplastic B-lymphoid cells.Cell Signal. 2019 Jan;53:68-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Cell Signal. 2019. PMID: 30244168 Free PMC article.
-
TRPM1.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:387-402. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_15. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756714 Review.
-
Cardiomyocyte calcium and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: friends or foes?Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004;59:141-68. doi: 10.1210/rp.59.1.141. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004. PMID: 14749501 Review.
Cited by
-
On the modulation of TRPM channels: Current perspectives and anticancer therapeutic implications.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 9;12:1065935. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1065935. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36844925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated Transcriptomic and Epigenomic Analysis Reveals Mechanisms Underlying Melanotic Spot Formation in Red Tilapia (Oreochromis spp.).Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 4;26(9):4370. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094370. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362607 Free PMC article.
-
Piezo1 promotes the progression of necrotizing enterocolitis by activating the Ca2(+)/CaMKII-dependent pathway.Commun Biol. 2025 Mar 12;8(1):417. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07821-6. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 40074811 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Calmodulin with TRPM: An Initiator of Channel Modulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 13;24(20):15162. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015162. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porcine transient receptor potential channel 1 promotes adipogenesis and lipid deposition.J Lipid Res. 2025 Jan;66(1):100718. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100718. Epub 2024 Dec 3. J Lipid Res. 2025. PMID: 39631563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang K., Fan J.i., Misra S. Acral Lentiginous Melanoma: Incidence and Survival in the United States, 2006–2015, an Analysis of the SEER Registry. J Surg Res. 2020;251:329–339. - PubMed
-
- Hayward N.K., Wilmott J.S., Waddell N., Johansson P.A., Field M.A., Nones K., et al. Whole-genome landscapes of major melanoma subtypes. Nature. 2017;545(7653):175–180. - PubMed
-
- Smalley K.S.M. Understanding melanoma signaling networks as the basis for molecular targeted therapy. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130(1):28–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

