Cryo-EM structure of the respiratory I + III2 supercomplex from Arabidopsis thaliana at 2 Å resolution
- PMID: 36585502
- PMCID: PMC9873573
- DOI: 10.1038/s41477-022-01308-6
Cryo-EM structure of the respiratory I + III2 supercomplex from Arabidopsis thaliana at 2 Å resolution
Abstract
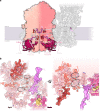
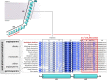
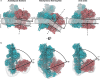
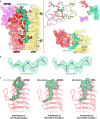
Protein complexes of the mitochondrial respiratory chain assemble into respiratory supercomplexes. Here we present the high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy structure of the Arabidopsis respiratory supercomplex consisting of complex I and a complex III dimer, with a total of 68 protein subunits and numerous bound cofactors. A complex I-ferredoxin, subunit B14.7 and P9, a newly defined subunit of plant complex I, mediate supercomplex formation. The component complexes stabilize one another, enabling new detailed insights into their structure. We describe (1) an interrupted aqueous passage for proton translocation in the membrane arm of complex I; (2) a new coenzyme A within the carbonic anhydrase module of plant complex I defining a second catalytic centre; and (3) the water structure at the proton exit pathway of complex III2 with a co-purified ubiquinone in the QO site. We propose that the main role of the plant supercomplex is to stabilize its components in the membrane.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








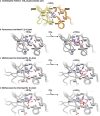
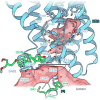
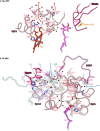

Comment in
-
Super-complex supercomplex.Nat Plants. 2023 Jan;9(1):5-6. doi: 10.1038/s41477-022-01329-1. Nat Plants. 2023. PMID: 36639556 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hatefi Y, Rieske JS. The preparation and properties of DPNH-cytochrome c reductase (complex I–III of the respiratory chain) Methods Enzymol. 1967;10:225–231. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(67)10044-X. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

