Limits on using the clock drawing test as a measure to evaluate patients with neurological disorders
- PMID: 36585622
- PMCID: PMC9805016
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-022-03035-z
Limits on using the clock drawing test as a measure to evaluate patients with neurological disorders
Abstract
Background: The Clock Drawing Test (CDT) is used as a quick-to-conduct test for the diagnosis of dementia and a screening tool for cognitive impairments in neurological disorders. However, the association between the pattern of CDT impairments and the location of brain lesions has been controversial. We examined whether there is an association between the CDT scores and the location of brain lesions using the two available scoring systems.
Method: One hundred five patients with brain lesions identified by CT scanning were recruited for this study. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) battery including the CDT were administered to all partcipants. To score the CDT, we used a qualitative scoring system devised by Rouleau et al. (1992). For the quantitative scoring system, we adapted the algorithm method used by Mendes-Santos et al. (2015) based on an earlier study by Sunderland et al. (1989). For analyses, a machine learning algorithm was used.
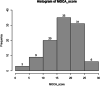
Results: Remarkably, 30% of the patients were not detected by the CDT. Quantitative and qualitative errors were categorized into different clusters. The classification algorithm did not differentiate the patients with traumatic brain injury 'TBI' from non-TBI, or the laterality of the lesion. In addition, the classification accuracy for identifying patients with specific lobe lesions was low, except for the parietal lobe with an accuracy of 63%.
Conclusion: The CDT is not an accurate tool for detecting focal brain lesions. While the CDT still is beneficial for use with patients suspected of having a neurodegenerative disorder, it should be cautiously used with patients with focal neurological disorders.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Location of brain lesions; Screening tool; The clock drawing test.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial, personal or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



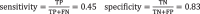



Similar articles
-
Quantitative and qualitative analyses of the clock drawing test in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease: evaluation of a modified scoring system.J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2011 Jun;24(2):108-18. doi: 10.1177/0891988711402349. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21546651
-
Psychometric properties of Clock Drawing Test and MMSE or Short Performance Test (SKT) in dementia screening in a memory clinic population.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2002 Mar;17(3):254-60. doi: 10.1002/gps.585. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2002. PMID: 11921154
-
Neural correlates of performance on the different scoring systems of the clock drawing test.Neurosci Lett. 2011 Jan 10;487(3):421-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.10.069. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Neurosci Lett. 2011. PMID: 21055445
-
The Times They Are a-Changin': Clock Drawing and Prediction of Dementia.J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2015 Jun;28(2):145-55. doi: 10.1177/0891988714554709. Epub 2014 Oct 14. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25319477 Review.
-
Scoring systems for the Clock Drawing Test: A historical review.Dement Neuropsychol. 2017 Jan-Mar;11(1):6-14. doi: 10.1590/1980-57642016dn11-010003. Dement Neuropsychol. 2017. PMID: 29213488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential cognitive and clinical improvements in Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder following hospitalization: A comparative analysis based on the Clock Drawing Test.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 8;20(7):e0325537. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325537. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40627645 Free PMC article.
-
Eye-tracking paradigms for the assessment of mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review.Front Psychol. 2023 Jul 20;14:1197567. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1197567. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37546488 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khan TK. Biomarkers in Alzheimer's Disease. Published: 2nd August 2016, Imprint: academic press, hardcover ISBN: 9780128048320. eBook ISBN: 9780128051474. 2016.
-
- Aprahamian I, Martinelli JK, Neri AL, Yassuda MS. The accuracy of the clock drawing test compared to that of standard screening tests for Alzheimer's disease: results from a study of Brazilian elderly with heterogeneous educational backgrounds. Int Psychogeriatr. 2010;22:64–71. doi: 10.1017/S1041610209991141. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

