Revisiting the therapeutic potential of gingerols against different pharmacological activities
- PMID: 36585999
- PMCID: PMC9803890
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-022-02372-7
Revisiting the therapeutic potential of gingerols against different pharmacological activities
Abstract
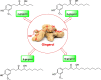
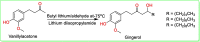
The rhizomes of ginger have been in use in many forms of traditional and alternative medicines. Besides being employed as condiment and flavoring agent, it is used in the treatment of nausea, osteoarthritis, muscle pain, menstrual pain, chronic indigestion, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer. Ginger rhizome contains volatile oils, phenolic compounds and resins, and characterization studies showed that [6]-gingerol, [6]-shogaol, and [6]-paradol are reported to be the pharmacologically active components. Gingerol is a major chemical constituent found as volatile oil in the rhizomes of ginger. It has several medicinal benefits and used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, nausea, cancer, and diabetes. Many studies have been carried out in various parts of the world to isolate and standardize gingerol for their use as a complementary medicine. The present review summarizes wide range of research studies on gingerol and its pharmacological roles in various metabolic diseases.
Keywords: Cancer; Ginger; Gingerol; Inflammation; Resins; Volatile oil; Zingiber officinale.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Abdu SB, Abdu F, Khalil WK. Ginger nanoparticles modulate the apoptotic activity in male rats exposed to dioxin-induced cancer initiation. Int J Pharmacol. 2017;13:946–957. doi: 10.3923/ijp.2017.946.957. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

