The impact of HER2-low status on response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in clinically HER2-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 36586066
- PMCID: PMC10202994
- DOI: 10.1007/s12094-022-03062-9
The impact of HER2-low status on response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in clinically HER2-negative breast cancer
Abstract
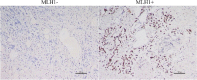
Purpose: Low expression of HER2 (HER2-low expression) in breast cancer (BC) has unique biological characteristics. However, whether HER2-low expression has an impact on neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) in HER2-negative breast cancer remains unclear.
Methods: This study reviewed the clinicopathological data of patients with BC treated with NACT at a single hospital from January 2018 to July 2022. Baseline patient characteristics, efficacy of NACT, and survival data were compared between the HER2-0 and HER2-low groups. The impact of NACT on HER2 status also was investigated. Subgroup analyses based on hormone receptor (HR) status were performed to explore the impact of HR signaling on HER2 status during chemotherapy.
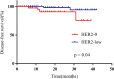
Results: The progesterone receptor-positive rate in the HER2-low group was significantly higher than that in HER2-0 group. The local treatment response of the HER2-low group was worse, but the disease-free survival rate of the HER2-low group was significantly better than that of the HER2-0 group. The proportion of patients with increased HER2 immunohistochemistry score after NACT was significantly higher in the HER2-0 group. Subgroup analysis showed that the efficacy of chemotherapy in HR + patients was significantly worse than in HR- patients, and HR + patients had a higher proportion of increased HER2 immunohistochemistry score after chemotherapy. Mechanistic studies suggested that MLH1 expression loss during chemotherapy might link HR signaling and regulation of HER2 expression.
Conclusions: We found that HER2-low expressing BC exhibits differential sensitivity to chemotherapy compared to HER2-0 expressing BC. The regulation of HER2 expression by HR signaling may mediate aspects of chemoresistance.
Keywords: Breast cancer; HER2-low expression; MLH1; Neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fehrenbacher L, Cecchini RS, Geyer CE, Jr, Rastogi P, Costantino JP, Atkins JN, et al. NSABP B-47/NRG oncology phase III randomized trial comparing adjuvant chemotherapy with or without trastuzumab in high-risk invasive breast cancer negative for HER2 by FISH and with IHC 1+ or 2. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:444–453. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01455. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ogitani Y, Aida T, Hagihara K, Yamaguchi J, Ishii C, Harada N, et al. DS-8201a, a novel HER2-targeting ADC with a Novel DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor, demonstrates a promising antitumor efficacy with differentiation from T-DM1. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:5097–5108. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2822. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous