Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in children with interstitial lung disease: Determine etiologies!
- PMID: 36588100
- PMCID: PMC10199423
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.26301
Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in children with interstitial lung disease: Determine etiologies!
Abstract
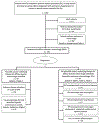
Objective: Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH) in children is a rare condition resulting from different underlying diseases. This study aimed at describing characteristics and diagnostic measures in children with ILD (children's interstitial lung disease, chILD) and DAH to improve the diagnostic approach by increasing clinician's awareness of diagnostic shortcomings.
Patients and methods: A retrospective data analysis of patients with ILD and DAH treated in our own or collaborating centers between 01/07/1997 and 31/12/2020 was performed. Data on clinical courses and diagnostic measures were systematically retrieved as case-vignettes and investigated. To assess suitability of diagnostic software-algorithms, the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) was revised and expanded to optimize conditions of its associated tool the "Phenomizer."
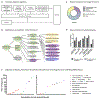
Results: For 97 (74%) of 131 patients, etiology of pulmonary hemorrhage was clarified. For 34 patients (26%), no underlying condition was found (termed as idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage, IPH). Based on laboratory findings or clinical phenotype/comorbidities, 20 of these patients were assigned to descriptive clusters: IPH associated with autoimmune features (9), eosinophilia (5), renal disease (3) or multiorgan involvement (3). For 14 patients, no further differentiation was possible.
Conclusion: Complete and sometimes repeated diagnostics are essential for establishing the correct diagnosis in children with DAH. We suggest assignment of patients with IPH to descriptive clusters, which may also guide further research. Digital tools such as the Phenomizer/HPO are promising, but need to be extended to increase diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: children's interstitial lung disease; diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage; human phenotype ontology; idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis; pediatric.
© 2023 The Authors. Pediatric Pulmonology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
There are no financial or personal relationships with other people or organizations that have influenced this work.
Figures
References
-
- States LJ, Fields JM. Pulmonary hemorrhage in children. Semin Roentgenol. 1998;33(2):174–86. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey S. Pulmonary hemorrhage/hemoptysis in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2004;37(6):476–84. - PubMed
-
- Lara AR, Schwarz MI. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Chest. 2010;137(5):1164–71. - PubMed
-
- Susarla SC, Fan LL. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage syndromes in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2007;19(3):314–20. - PubMed
-
- Eber E, Midula F. ERS Handbook of Paediatric Respiratory Medicine: EUROPEAN RESPIRATORY SOCIETY; 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

