Characterization of Virulence-Associated Traits in Mycoplasma penetrans Strains Acting as Likely Etiological Agents of Idiopathic Nongonococcal Urethritis
- PMID: 36588346
- PMCID: PMC10319971
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiac505
Characterization of Virulence-Associated Traits in Mycoplasma penetrans Strains Acting as Likely Etiological Agents of Idiopathic Nongonococcal Urethritis
Abstract
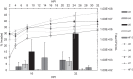
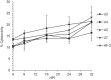
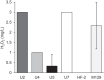
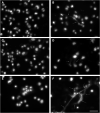
Mycoplasma penetrans is an emerging pathogen with a reduced genome. This bacterium has only previously been cultured from individuals with chronic immunodeficiencies. Here we report the characteristics of 4 M. penetrans isolates from the urine of immunocompetent males with nongonococcal urethritis, in comparison with strain HF-2 from an immunocompromised patient. Several features exhibited distinct differences between these isolates and HF-2. Unlike HF-2, all 4 were resistant to azithromycin. They exhibited greater sialic acid-dependent binding to erythrocytes, gliding motility speed, and H2O2 production than HF-2. All new isolates produced thinner capsules than HF-2. Invasiveness varied, with some isolates being more invasive than HF-2 and some less invasive. Cytotoxicity to HeLa cells was similar to HF-2, and all strains could clear extracellular traps produced by innate immune cells. We conclude that subtle differences among M. penetrans strains may be critical for this organism to establish an infection in an otherwise healthy individual.
Keywords: Mycoplasma penetrans; idiopathic urethritis; nongonococcal urethritis.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts of interest. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Urethral Microbiota in Men: Association of Haemophilus influenzae and Mycoplasma penetrans With Nongonococcal Urethritis.Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Oct 5;73(7):e1684-e1693. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1123. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 32750107 Free PMC article.
-
Failure to detect Mycoplasma fermentans, Mycoplasma penetrans, or Mycoplasma pirum in the urethra of patients with acute nongonococcal urethritis.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1996 Feb;15(2):169-71. doi: 10.1007/BF01591493. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1996. PMID: 8801092
-
Mycoplasma genitalium: another important pathogen of nongonococcal urethritis.J Urol. 2002 Mar;167(3):1210-7. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(05)65268-8. J Urol. 2002. PMID: 11832700 Review.
-
Association of Mycoplasma genitalium persistence in the urethra with recurrence of nongonococcal urethritis.Sex Transm Dis. 2001 Aug;28(8):472-6. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200108000-00010. Sex Transm Dis. 2001. PMID: 11473221
-
Genital mycoplasmas, including Mycoplasma genitalium, as sexually transmitted agents.Int J STD AIDS. 2002 Feb;13(2):79-85. doi: 10.1258/0956462021924695. Int J STD AIDS. 2002. PMID: 11839161 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of Mycoplasma penetrans in Urogenital Samples From Men Screened for Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023 Apr 4;10(4):ofad180. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofad180. eCollection 2023 Apr. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37082616 Free PMC article.
-
Mycoplasma penetrans urethritis in men. A case-control study.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 19;16:1565685. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1565685. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40177480 Free PMC article.
-
Role of P38 lipoprotein in Mycoplasma penetrans adhesion to human urothelial cells.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Aug 30;25(1):566. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04215-w. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40885928 Free PMC article.
-
Screening the receptors for Mycoplasma penetrans P35 lipoprotein and characterization of its functional binding domains.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Mar 17;15:1525789. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1525789. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40166371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lo SC, Hayes MM, Wang RYH, Pierce PF, Kotani H, Shih JWK. Newly discovered mycoplasma isolated from patients infected with HIV. Lancet 1991; 338:1415–8. - PubMed
-
- Lo SC, Hayes MM, Kotani H, et al. . Adhesion onto and invasion into mammalian cells by Mycoplasma penetrans: a newly isolated mycoplasma from patients with AIDS. Mod Pathol 1993; 6:276–80. - PubMed
-
- Wang RYH, Hayes MM, Wear DJ, et al. . High frequency of antibodies to Mycoplasma penetrans in HIV-infected patients. Lancet 1992; 340:1312–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

