A combination of the Modified Early Warning Score and the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale as a triage tool in patients with infection
- PMID: 36588422
- PMCID: PMC10090726
- DOI: 10.15441/ceem.22.339
A combination of the Modified Early Warning Score and the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale as a triage tool in patients with infection
Abstract
Objective: We evaluated the utility of the Korean Modified Early Warning Score (KMEWS), which combines the Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS) and the Korean Triage and Acuity Scale (KTAS), as a triage tool to screen for infection in patients who visit the emergency department.
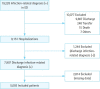
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed data extracted from electronic medical records. Patients aged ≥18 years with an infection who were admitted to the hospital via the emergency department between January 2018 and December 2019 were eligible for inclusion. The KMEWS score was calculated as the sum of the KTAS level and the MEWS score. We generated receiver operating characteristic curves and determined the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for the KMEWS, KTAS, MEWS, and Mortality in Emergency Department Sepsis (MEDS) scales. The primary outcome was septic shock, and secondary outcomes were intensive care unit admission and in-hospital mortality.
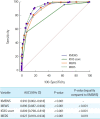
Results: The AUC values (95% confidence interval) for predicting septic shock were as follows: KMEWS, 0.910 (0.902-0.918); MEWS, 0.896 (0.887-0.904); KTAS score, 0.809 (0.798-0.819); and MEDS, 0.927 (0.919-0.934). The AUC values (95% confidence interval) for predicting in-hospital mortality were as follows: KMEWS, 0.752 (0.740-0.764); MEWS, 0.717 (0.704-0.729); KTAS score, 0.764 (0.752-0.776); and MEDS, 0.844 (0.834-0.854). The AUC values (95% confidence interval) for predicting intensive care unit admission were as follows: KMEWS, 0.826 (0.816-0.837); MEWS, 0.782 (0.770-0.793); KTAS score, 0.821 (0.810-0.831); and MEDS, 0.839 (0.829-0.849).
Conclusion: The KMEWS, which is a combination of the MEWS and the KTAS scores, might be a useful triage tool in emergency department patients who present with infection, particularly for predicting septic shock.
Keywords: Critical care; Hospital emergency service; Mortality; Septic shock; Triage.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–10. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Moss M. The effect of age on the development and outcome of adult sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Gauer RL. Early recognition and management of sepsis in adults: the first six hours. Am Fam Physician. 2013;88:44–53. - PubMed
-
- Ferrer R, Artigas A, Suarez D, et al. Effectiveness of treatments for severe sepsis: a prospective, multicenter, observational study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:861–6. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

