Perceptions of healthcare professionals and patients on the role of the pharmacist in TB management in Pakistan: A qualitative study
- PMID: 36588713
- PMCID: PMC9798110
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.965806
Perceptions of healthcare professionals and patients on the role of the pharmacist in TB management in Pakistan: A qualitative study
Abstract
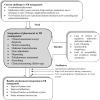
Background: Globally, tuberculosis (TB) is the second major cause of death from infectious diseases, particularly in developing countries. A multidisciplinary approach to the management of TB may help to curb the disease burden. Objective: The objective of this study was to outline the perceptions of healthcare professionals and patients regarding the potential role of pharmacists in TB management in Pakistan. Method: This was a large-scale qualitative study conducted at the Chest Disease Unit (CDU) of the Bahawal Victoria Hospital (BVH), Punjab, Pakistan. Data were collected through semi-structured interviews with physicians, pharmacists, and patients recruited using a mix of convenient and snowball sampling. The sample size was decided through standard saturation point criteria. All interviews were audio recorded and transcribed verbatim. The data were analyzed to draw conclusions using a thematic analysis approach. Results: Analysis of the data yielded 19 categories and seven themes. Physicians considered pharmacists qualified healthcare professionals, whereas patients considered them merely dispensers. Inventory management and dispensing of medicines were considered as major responsibilities of pharmacists. Physicians were extremely overburdened and wanted to delegate certain duties to pharmacists, subject to their prior extensive trainings. However, most of the physicians were unaware of the legal scope of pharmacy practice in Pakistan. With regard to the potential duties of pharmacists, physicians, pharmacists, and patients (patients-upon explaining the potential roles during the interview) endorsed monitoring, counseling, medicine brand selection, dose adjustment, inventory management, dispensing, and polypharmacy assessment as their potential roles. In view of all stakeholders, the rationale for integrating pharmacists in TB management included overburdened physicians, sub-standard patient care, medication safety issues, and patient dissatisfaction. The healthcare professionals highlighted that the major barriers to integrating pharmacists within the TB management system were limited interest of regulatory authorities and policy makers, followed by inadequate training and experience-driven questionable competency of pharmacists. Conclusion: The study participants acknowledged the potential role of pharmacists in TB management. However, it was emphasized that healthcare policy makers should devise strategies to overcome the underlying barriers before assigning medicine-related clinical roles to pharmacists.
Keywords: FIP; National Tuberculosis Control Program of Pakistan; Pakistan; multidisciplinary approach; patient centered care; pharmacist; tuberculosis management.
Copyright © 2022 Atif, Munir, Malik, Al-Worafi, Mushtaq and Ahmad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Can we involve pharmacists as direct service providers for people with tuberculosis? A narrative review of current evidence.Explor Res Clin Soc Pharm. 2025 May 18;19:100613. doi: 10.1016/j.rcsop.2025.100613. eCollection 2025 Sep. Explor Res Clin Soc Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40502458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors affecting patients' knowledge about dispensed medicines: A Qualitative study of healthcare professionals and patients in Pakistan.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 1;13(6):e0197482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197482. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29856753 Free PMC article.
-
A qualitative study to explore the role of pharmacists in healthy weight management in adults in Pakistan: current scenario and future perspectives.BMC Health Serv Res. 2020 Jun 15;20(1):541. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05419-8. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. PMID: 32539709 Free PMC article.
-
Community pharmacists as antibiotic stewards: A qualitative study exploring the current status of Antibiotic Stewardship Program in Bahawalpur, Pakistan.J Infect Public Health. 2020 Jan;13(1):118-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2019.07.003. Epub 2019 Sep 20. J Infect Public Health. 2020. PMID: 31548165
-
The development of a role description and competency map for pharmacists in an interprofessional care setting.Int J Clin Pharm. 2019 Apr;41(2):391-407. doi: 10.1007/s11096-019-00808-4. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Int J Clin Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30879217 Review.
Cited by
-
Multidisciplinary tuberculosis care: leveraging the role of hospital pharmacists.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023 Nov;10(1):e001887. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2023-001887. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37949612 Free PMC article.
-
Can we involve pharmacists as direct service providers for people with tuberculosis? A narrative review of current evidence.Explor Res Clin Soc Pharm. 2025 May 18;19:100613. doi: 10.1016/j.rcsop.2025.100613. eCollection 2025 Sep. Explor Res Clin Soc Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40502458 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adnan S., Tanwir S., Abbas A., Beg A. E., Sabah A., Safdar H., et al. (2014). Perception of physicians regarding patient counseling by pharmacist: A blend of quantitative and qualitative insight. Int. J. Pharm. Ther. 5 (2), 117–121.
-
- Atif M., Ahmad M., Saleem Q., Curley L., Qamar-uz-Zaman M., Babar Z-U-D. (2017). “Pharmaceutical policy in Pakistan,” in Pharmaceutical policy in countries with developing healthcare systems. Editor Babar Z-U-D. (Cham: Springer International Publishing; ), 25–44. 10.1007/978-3-319-51673-8_3 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources